Lessor Company leases small computers on three-year leases at the end of which the residual value
is not material in amount.Rents are collected at year-end.On January 1, 2014, Lessor signed a 3-year lease with Lessee Company that called for annual rents of $12,063, which was a return to
Lessor of 10% on the $30,000 cost (market value at date of lease).Assume the lease qualifies as a direct financing lease to the lessor and a finance lease to the lessee.There was no bargain purchase option or residual value.The lessee's incremental borrowing rate is 12%.
(a)Complete the following amortization schedule for the lease.Round to the nearest dollar. 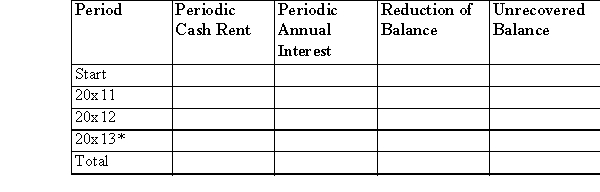 * May have slight rounding error.
* May have slight rounding error.
(b)Can both the lessor and lessee use the amortization schedule values in this instance? Yes ________ No ________
Explain why _.
(c)Give the entries for the lessor and lessee on the following dates (assume the accounting period ends December 31).Use the abbreviated account titles.
January 1, 2014-Inception of the lease:
 December 31, 2014-Interest date and end of accounting period (give all entries except closing entries):
December 31, 2014-Interest date and end of accounting period (give all entries except closing entries):
Definitions:
Target Audience
A specific group of consumers identified as the intended recipients of an advertising or marketing message, based on shared characteristics.
Advertising Program
An advertising program is a comprehensive plan that outlines the marketing and communication strategies, including media channels and creative concepts, used to achieve advertising objectives.
Fear Appeal
A marketing strategy that uses the element of fear to motivate the audience to take a certain action or adopt a specific behavior.
Tune Out
The act of ignoring or choosing not to engage with a message, advertisement, or piece of content.
Q15: If the corporation purchases common treasury stock,
Q15: Explain what is meant by off-balance sheet
Q32: At the end of 2014, interest on
Q33: Current costs of a pension plan that
Q38: Last year, TUV had 40,000 $15 par,
Q50: Steps in calculating diluted EPS include the
Q103: Lamont Company leases computers for a three-year
Q131: Under ASPE, forfeitures which occur under a
Q149: On January 10, 2013, ZOE Corporation declared
Q175: On December 31, 2015, JKL leased a