SCENARIO 11-12
A student team in a business statistics course designed an experiment to investigate whether the brand
of bubblegum used affected the size of bubbles they could blow. To reduce the person-to-person
variability, the students decided to use a randomized block design using themselves as blocks.
Four brands of bubblegum were tested. A student chewed two pieces of a brand of gum and then blew
a bubble, attempting to make it as big as possible. Another student measured the diameter of the
bubble at its biggest point. The following table gives the diameters of the bubbles (in inches) for the
16 observations. 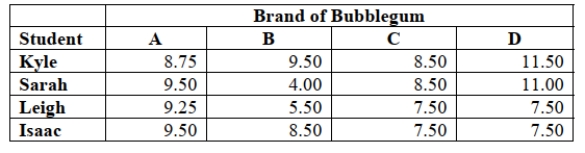
-Referring to Scenario 11-12, the null hypothesis for the randomized block F test for the difference in the means is a)
b)
c)
d)
Definitions:
Secondary Data Analysis
The process of analyzing data that was collected by someone else for a different purpose.
Ethical Violations
Actions or behaviors that breach established codes of conduct or moral principles, often resulting in professional or legal consequences.
Experiments
are systematic investigations conducted to test hypotheses, involving controlled variables to determine effects and outcomes.
Qualitative Research
A data-collection process that examines and interprets nonnumerical material.
Q8: Test the null hypothesis of independence
Q18: What is the relationship between diamond price
Q55: The staff of a test kitchen
Q73: The expected return of a two-asset portfolio
Q83: The sign test can not be used
Q88: In a study of feeding behavior,
Q162: The McNemar test is used to determine
Q164: Which of the following is most likely
Q176: Referring to Scenario 11-13, the amount of
Q179: Referring to Scenario 8-12, what is the