Solve the problem. Refer to the table if necessary. 2013 Marginal Tax Rates, Standard Deductlons, and Exemptlons**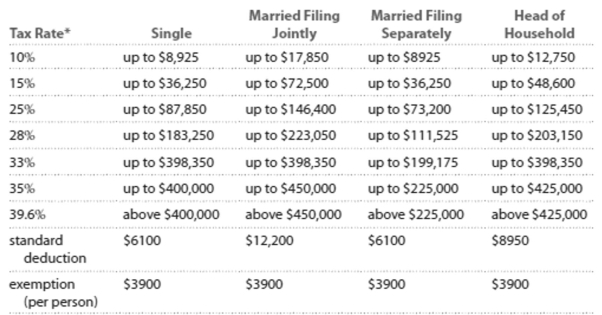
- Each higher marginal rate begins where the prior one leaves off. For example, for a single person, the marginal rate affects income starting at , which is where the rate leaves off, and continuing up to \$36,250.
" This table ignores the effects of (i) exemption and deduction phase-outs that apply to high-income taxpayers and (ii) the alternative minimum tax (AMT) that affects many middle- and high-income taxpayers.
-Kyle is single and earned wages of $34,036. He received $362 in interest from a savings account. He contributed $549 to a tax-deferred retirement plan. He had $405 in itemized deductions from
Charitable contributions. Calculate his adjusted gross income.
Definitions:
Overhead Absorption Rate
The rate at which indirect costs are allocated to produced goods or services.
ABC System
Activity-Based Costing; a method of assigning overhead and indirect costs to specific products or projects, based on their usage of activities.
Single-Base Allocation
A cost allocation method where overhead costs are distributed based on a single criterion or cost driver.
Cost Difference
The variance between the actual cost and the standard or expected cost of an item or activity.
Q1: With tax-exempt investments, you never have to
Q13: <span class="ql-formula" data-value="984 \div 0.00869 ; 3"><span
Q29: You are married filing jointly and have
Q31: The average annual precipitation in Tewinville is
Q33: <span class="ql-formula" data-value="8 n - 10 =
Q81: Choice 1: 30 -year fixed rate
Q85: The average weight of 100 college-age women,
Q155: Number of days worked last year by
Q230: The political affiliations of residents of a
Q252: Calculate the monthly payment for a home