Solve the problem. Refer to the table if necessary. 2013 Marginal Tax Rates, Standard Deductions, and Exemptlons**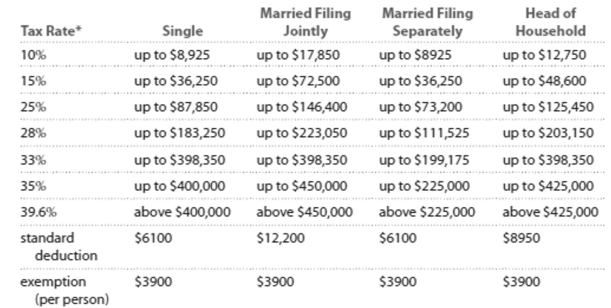
- Each higher marginal rate begins where the prior one leaves off. For example, for a single person, the marginal rate affects income starting at , which is where the rate leaves off, and continuing up to .
" This table ignores the effects of (i) exemption and deduction phase-outs that apply to high-income taxpayers and (ii) the alternative minimum tax (AMT) that affects many middle- and high-income taxpayers.
-Your deductible expenditures $4146 for contributions to charity and $635 for state income taxes. Your filing status entitles you to a standard deduction of $6100. Should you itemize your
Deductions rather than claiming the standard deduction? If so, what is the difference?
Definitions:
Nominal Exchange Rate
The rate at which one country's currency can be exchanged for another country's currency, not adjusted for inflation.
Real Exchange Rate
The real exchange rate compares the relative price of goods and services between countries, adjusted for differences in price levels.
Nominal Exchange Rate
The rate at which one country's currency can be exchanged for another country's currency.
Real Exchange Rate
An exchange rate that has been adjusted for the relative purchasing power of the two currencies, reflecting the quantity of goods and services one currency can buy in another country.
Q12: You return from a trip with 3400
Q14: A researcher finds a negative correlation between
Q30: Find the scale ratio for a map
Q58: A $49,433 deposit in an account with
Q62: The following table shows the number
Q63: Computer sales for a certain company have
Q121: You are interested in the degree of
Q177: Suppose that you need a loan
Q197: A meal in a restaurant cost $45
Q242: We will never be able to send