Solve the problem. Refer to the table if necessary. 2013 Marginal Tax Rates, Standard Deductlons, and Exemptlons**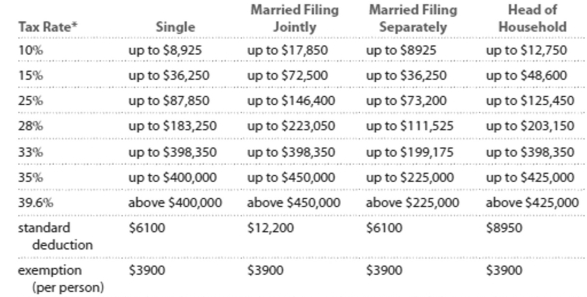
"Each higher marginal rate begins where the prior one leaves off. For example, for a single person, the marginal rate affects income starting at , which is where the rate leaves off, and continuing up to .
" "This table ignores the effects of (i) exemption and deduction phase-outs that apply to high-income taxpayers and (ii) the alternative minimum tax (AMT) that affects many middle-and high-income taxpayers.
-Kelly and Kurt are married filing jointly with a taxable income of $92,745. Calculate the amount of tax owed.
Definitions:
Banks
Financial institutions that accept deposits from the public, lend money, and offer various other financial services.
National Railroad Network
A comprehensive system of railway lines and routes covering a national territory, facilitating passenger and freight transport.
Civil War
An internal conflict between factions or regions within the same country, where the factions fight for political control, ethnic or religious reasons, or territorial independence.
Protective Tariffs
Taxes imposed on imported goods to protect domestic industries from foreign competition by making imported goods more expensive.
Q14: Number of siblings of adults in the
Q20: <img src="https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB3069/.jpg" alt=" A)
Q47: <span class="ql-formula" data-value="8 x = 56"><span class="katex"><span
Q57: What is the compound interest formula
Q101: Kelly earned wages of $87,240, received $4814
Q106: A curved bridge rises over a river,
Q111: Chuck has saved $364 at the bank.
Q119: Abe, Boris, Cal, and David all proposed
Q204: A researcher wants to determine the level
Q222: How do lawyers' salaries compare to doctors'