Homelessness is a problem in many large U.S. cities. To better understand the problem, a
multiple regression was used to model the rate of homelessness based on several
explanatory variables. The following data were collected for 50 large U.S. cities. The
regression results appear below. 
Unemployment percent of residents unemployed
Temperature average yearly temperature (in degrees F.)
Vacancy percent of housing that is unoccupied
Rent Control indicator variable, city has rent control, no rent control
Dependent variable is Homeless
squared squared (adjusted)
with degrees of freedom
a. Using a 5% level of significance, which variables are associated with the number of
homeless in a city?
b. Explain the meaning of the coefficient of temperature in the context of this problem.
c. Explain the meaning of the coefficient of rent control in the context of this problem.
d. Do the results suggest that having rent control laws in a city causes higher levels of
homelessness? Explain.
e. If we created a new model by adding several more explanatory variables, which statistic
should be used to compare them - the R2 or the adjusted R2 ? Explain.
f. Using the plots below, check the regression conditions. 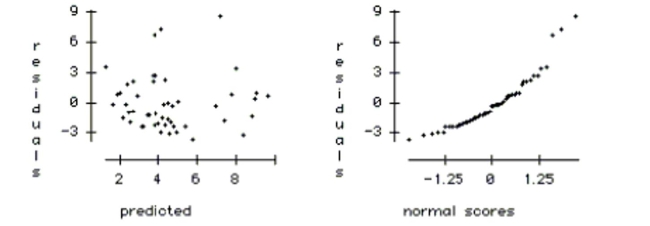
Definitions:
World Bank
An international financial institution that provides loans and grants to the governments of poorer countries for the purpose of pursuing capital projects.
Privatization
The process of transferring ownership or control of a business or service from the government to private individuals or organizations.
Transitional Economies
These are countries changing from a centrally planned economy towards a more market-oriented economy.
Global Economic Fluctuations
Variations in economic activity, such as growth and recession, experienced across the world economy.
Q17: Identify the factors and levels.
Q18: For each of 200 randomly selected cities,
Q38: What is the standard deviation of the
Q58: A bus company claims that in the
Q60: Describe how you will use a random
Q65: In a clinical trial for a new
Q66: In the larger sample the proportion of
Q77: Suppose that a device advertised to
Q79: BatCo, a company that sells batteries, claims
Q122: Sleep Do more than 50% of U.S.