The bigger the stop sign, the more expensive it is. Here is a graph of the height of a sign in inches versus its cost in dollars.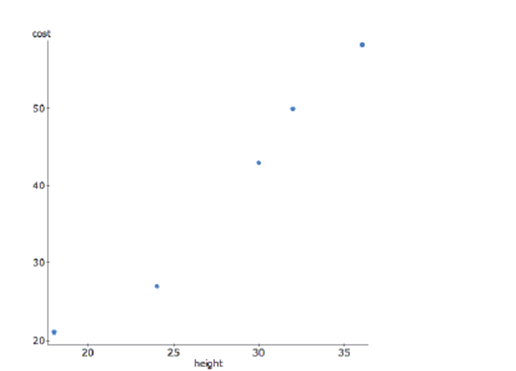
To achieve linearity, the data was transformed using a square root function of cost. Here are the results and a residual plot.Dependent Variable: sqrt(cost)
(correlation coefficient)
s: 0.2141

-Use your equation to predict the cost of a 48" stop sign.
Definitions:
Government Intervention
Actions taken by a government to influence or directly control some aspects of the economy or society.
Prisoners' Dilemma
The Prisoners' Dilemma is a standard example of a game analyzed in game theory that shows why two completely rational individuals might not cooperate, even if it appears that it is in their best interest to do so.
Repeatedly Interact
Engaging in continuous or frequent exchanges or encounters between individuals or entities.
Q111: A professor has kept records on grades
Q144: Which statement about re-expressing data is not
Q352: What is the probability that the tenth
Q354: Describe to the group an advantage and
Q370: Use your equation to predict the cost
Q437: Since r2 is not 100%, there must
Q472: What is the probability that none of
Q525: Test an appropriate hypothesis and state your
Q714: The correlation coefficient between high school grade
Q729: The two samples whose statistics are