Assume that after you estimate the risk neutral model for the continously compounded rate you arrive at the tree presented at the beginning of this chapter. There is equal probability of moving up or down on the tree. Price a ?oor that pays at time t + 1 the following cash ?ow: 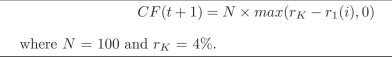
Definitions:
APR
Annual Percentage Rate, which represents the annual cost of borrowing or the annual yield from an investment.
Interest Rate
The financial percentage of the principal demanded by a lender for giving a borrower access to resources.
Pure Discount Loan
A loan where the borrower receives a single lump sum payment at maturity instead of periodic payments, with interest incorporated in the repayment amount.
Present Value Problem
A calculation to determine the current value of a future amount of money or stream of cash flows given a specified rate of return.
Q1: Why are Hull-White prices for call options
Q2: When computing ∂V/∂r, what is the difference
Q7: Using the information provided at the beginning
Q11: Calculate the convexity of the following portfolio:
Q15: Compute F (0, 3, 5), f2(0, 3,
Q19: What is an American Call option?
Q20: Inflation is defined as a decline in
Q24: <span class="ql-formula" data-value="f ( x ) =
Q35: The marginal revenue curve shows the relationship
Q67: Which of the following features is typically