Consider two different implementations, M1 and M2, of the same instruction set. There are three classes of instructions (A, B, and C) in the instruction set. M1 has a clock rate of 80 MHz and M2 has a clock rate of 100 MHz. The average number of cycles for each instruction class and their frequencies (for a typical program) are as follows: 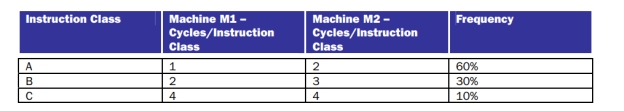 (a) Calculate the average CPI for each machine, M1, and M2.
(a) Calculate the average CPI for each machine, M1, and M2.
(b) Calculate the average MIPS ratings for each machine, M1 and M2.
(c)Which machine has a smaller MIPS rating ? Which individual instruction class CPI do you need to change, and by how much, to have this machine have the same or better performance as the machine with the higher MIPS rating (you can only change the CPI for one of the instruction classes on the slower machine)?
Definitions:
Civil Citizenship
Refers to the status conferred upon individuals by a state, entitling them to rights and responsibilities within that state's legal framework.
Political Citizenship
Refers to the status and rights of individuals within a political entity, including participation in political processes and the right to vote.
Social Citizenship
The rights, duties, and entitlements associated with being a member of a society, allowing individuals access to social services, healthcare, and education, fostering a sense of belonging and participation.
Routine Collective Actions
The regular, patterned, and unexceptional activities performed by groups of individuals that reinforce social norms and cohesion.
Q1: Given the declaration Circle[] x = new
Q3: Show the BST after inserting 45, 43,
Q9: Describe the function of the revision status
Q12: Calculate the performance of a processor taking
Q19: The results of a leadership situation can
Q36: Which of the following pairs are related
Q38: Describe the work done by electrical drafters.
Q43: Define exporting.
Q55: Which of the following compounds do not
Q124: Discuss the results of designing a part