TABLE 16-12
A local store developed a multiplicative time-series model to forecast its revenues in future quarters, using quarterly data on its revenues during the 4-year period from 2005 to 2009. The following is the resulting regression equation:
log₁₀ 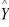 = 6.102 + 0.012 X - 0.129 Q₁ - 0.054 Q₂ + 0.098 Q₃
= 6.102 + 0.012 X - 0.129 Q₁ - 0.054 Q₂ + 0.098 Q₃
where 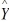 is the estimated number of contracts in a quarter.
is the estimated number of contracts in a quarter.
X is the coded quarterly value with X = 0 in the first quarter of 2005.
Q₁ is a dummy variable equal to 1 in the first quarter of a year and 0 otherwise.
Q₂ is a dummy variable equal to 1 in the second quarter of a year and 0 otherwise.
Q₃ is a dummy variable equal to 1 in the third quarter of a year and 0 otherwise.
-Referring to Table 16-12, in testing the significance of the coefficient for Q₁ in the regression equation (-0.129) which has a p-value of 0.492. Which of the following is the best interpretation of this result?
Definitions:
Scatterplot
A graphical representation using dots to show the relationship between two quantitative variables.
Correlation
A gauge that determines the extent of simultaneous variations between two or more variables.
Lurking Variable
A variable that is not directly measured but affects the variables of interest in a study, potentially confounding the results.
Heights
Refers to the measurement of vertical length, either of an individual or object, typically measured from base to top.
Q13: Referring to Table 16-4, a centered 3-year
Q29: Referring to Table 17-9, an R chart
Q44: After estimating a trend model for annual
Q53: Changes in the system to reduce common
Q72: To determine the probability of getting at
Q73: Referring to Table 14-17 Model 1, the
Q91: Referring to Table 17-10, a c chart
Q152: Referring to Table 9-1, if you select
Q254: Referring to Table 9-3, if you select
Q272: Referring to Table 14-17 Model 1, we