For the strain of the flu modeled by the differential equations 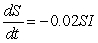
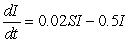 ,
,
does the disease spread if initially 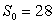 ?
?
Definitions:
Random Variables
A mathematical representation of a quantitative variable whose value depends on outcomes of a random phenomenon.
Continuous Probability Distribution
A type of probability distribution where the possible outcomes form a continuous range, and probabilities are assigned over intervals rather than distinct events.
Wider
Implying an increase in breadth or extent, often used in a comparative context to describe physical dimensions or the scope of analysis.
Uniform Probability Distribution
A type of probability distribution where all outcomes are equally likely to occur within a defined interval.
Q2: In 2009, during the height of the
Q10: In Windsor, Ontario, a Big Mac from
Q16: Let C(q) represent the cost, R(q), the
Q20: The first derivative of <img src="https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB8190/.jpg" alt="The
Q25: Which of the following can be affected
Q28: A quantity y satisfies the differential equation
Q69: The demand, D, for gasoline at Station
Q79: The average cost per item to produce
Q127: Below is a contour diagram depicting D,
Q178: Find the derivative of <img src="https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB8190/.jpg" alt="Find