Angular momentum: A 500-g particle is located at the point 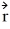 = 4m
= 4m  + 3m
+ 3m  - 2m
- 2m  and is moving with a velocity
and is moving with a velocity 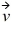 = 5 m/s
= 5 m/s  - 2m/s
- 2m/s  + 4 m/s
+ 4 m/s  . What is the angular momentum of this particle about the origin?
. What is the angular momentum of this particle about the origin?
Definitions:
Interest Expense
The cost incurred by an entity for borrowed funds, reflected as a charge against earnings on the income statement.
Income Statement
A financial statement that reports a company's financial performance over a specific accounting period, detailing revenues, expenses, and profits or losses.
Convertible Bond
A convertible bond is a type of bond that the holder can convert into a specified number of shares of common stock in the issuing company, usually at certain times during its life.
Common Stock
A type of equity security that represents ownership in a corporation and entitles the holder to vote at shareholder meetings and receive dividends.
Q2: Minicore disease is reported with code _.
Q6: Sickle-cell thalassemia with acute chest syndrome is
Q15: Slanted surfaces with friction: In the figure,
Q22: Hubble's law: Estimate the speed of a
Q23: Tensile stress and strain: A very light
Q25: The first chapter in ICD-10-CM is titled
Q29: Work: A graph of the force on
Q30: The instructional notes in the Tabular List
Q44: Momentum: A firecracker breaks up into several
Q132: Newton's second law: The figure shows an