Matrejek Corporation has two manufacturing departments--Forming and Customizing. The company used the following data at the beginning of the year to calculate predetermined overhead rates:
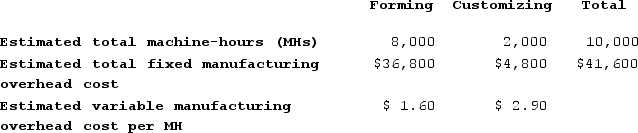 During the most recent month, the company started and completed two jobs--Job D and Job K. There were no beginning inventories. Data concerning those two jobs follow:
During the most recent month, the company started and completed two jobs--Job D and Job K. There were no beginning inventories. Data concerning those two jobs follow:
 Required:a. Assume that the company uses a plantwide predetermined manufacturing overhead rate based on machine-hours and uses a markup of 50% on manufacturing cost to establish selling prices. Calculate the selling price for Job D.b. Assume that the company uses a plantwide predetermined manufacturing overhead rate based on machine-hours and uses a markup of 50% on manufacturing cost to establish selling prices. Calculate the selling price for Job K.c. Assume that the company uses departmental predetermined overhead rates with machine-hours as the allocation base in both production departments. Further assume that the company uses a markup of 50% on manufacturing cost to establish selling prices. Calculate the selling price for Job D.d. Assume that the company uses departmental predetermined overhead rates with machine-hours as the allocation base in both production departments. Further assume that the company uses a markup of 50% on manufacturing cost to establish selling prices. Calculate the selling price for Job K.
Required:a. Assume that the company uses a plantwide predetermined manufacturing overhead rate based on machine-hours and uses a markup of 50% on manufacturing cost to establish selling prices. Calculate the selling price for Job D.b. Assume that the company uses a plantwide predetermined manufacturing overhead rate based on machine-hours and uses a markup of 50% on manufacturing cost to establish selling prices. Calculate the selling price for Job K.c. Assume that the company uses departmental predetermined overhead rates with machine-hours as the allocation base in both production departments. Further assume that the company uses a markup of 50% on manufacturing cost to establish selling prices. Calculate the selling price for Job D.d. Assume that the company uses departmental predetermined overhead rates with machine-hours as the allocation base in both production departments. Further assume that the company uses a markup of 50% on manufacturing cost to establish selling prices. Calculate the selling price for Job K.
Definitions:
Bilateral Contract
A legal agreement in which both parties make promises to perform certain actions or obligations.
Unilateral Contract
An agreement where one party makes a promise in exchange for an act by another party, becoming binding once the act is performed.
AIG
American International Group, Inc., a multinational finance and insurance corporation with operations in more than 80 countries and jurisdictions.
Liquidated Debt
A debt for which the exact monetary value has been determined and acknowledged by all parties involved.
Q168: Meenach Corporation uses a job-order costing system
Q174: Manufacturing overhead includes:<br>A) all direct material, direct
Q218: If the activity level increases, then one
Q230: Claybrooks Corporation has two manufacturing departments--Casting and
Q257: Dake Corporation's relevant range of activity is
Q258: Njombe Corporation manufactures a variety of products.
Q286: Sonneborn Corporation has two manufacturing departments--Molding and
Q290: Gerstein Corporation uses a job-order costing system
Q303: Data from Estrin Corporation's most recent balance
Q314: Garza Corporation has two production departments, Casting