In one-way ANOVA, suppose that there are three treatments with 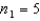 ,
, 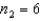 and
and 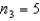 . Then the rejection region for this test at the 5% level of significance is:
. Then the rejection region for this test at the 5% level of significance is:
Definitions:
Conjunction Fallacy
A logical fallacy that occurs when people assume that specific conditions are more probable than a single general one.
Base Rate Fallacy
A cognitive error where people wrongly judge the likelihood of a situation by ignoring general statistical information and focusing on specific information.
Gambler's Fallacy
The erroneous belief that if something happens more frequently than normal during a given period, it will happen less frequently in the future, or vice versa.
Overestimation Fallacy
The cognitive bias of overestimating one's own abilities, performance, level of control, or chances of success.
Q21: The purpose of designing a randomized block
Q44: What is the effect of multicollinearity on
Q46: In testing <img src="https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB8220/.jpg" alt="In testing
Q65: If the probability of committing a Type
Q76: An automobile manufacturer would like to know
Q93: Use the following partial output and residual
Q116: In a randomized block design of ANOVA,
Q118: A two-tailed hypothesis test of the population
Q150: The assumption(s) for <img src="https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB8220/.jpg" alt="The assumption(s)
Q210: From a sample of 400 items, 14