Figure: Comparative Advantage
Eastland and Westland produce only two goods, boxes of peaches and boxes of oranges, and this figure shows each nation's production possibility frontier for the two goods. 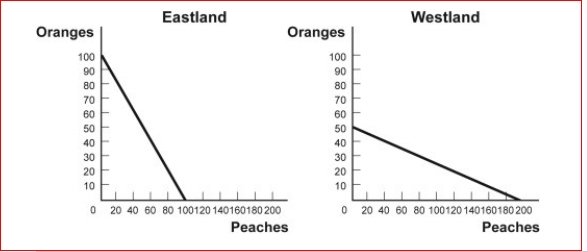 (Figure: Comparative Advantage) Look at the figure Comparative Advantage.The opportunity cost of producing 1 box of oranges for Eastland is:
(Figure: Comparative Advantage) Look at the figure Comparative Advantage.The opportunity cost of producing 1 box of oranges for Eastland is:
A.1 box of peaches.
B.1/4 box of peaches.
C.4 boxes of peaches.
D.10 boxes of peaches.
Definitions:
Cash-Generating Units
the smallest identifiable group of assets that generates cash inflows largely independent of the cash inflows from other assets or groups of assets.
Business Combination
The process of uniting multiple businesses into one single entity, often through acquisitions or mergers.
Unrealized Profits
Gains on assets that have appreciated in value but have not been sold, and therefore, the gains are not reflected in the financial results as actual income.
Upstream Sales
Transactions in which a subsidiary sells goods or services to its parent company, often analyzed for transfer pricing and tax considerations.
Q9: It is better to go to court
Q10: When drafting a hospitality contract, you should
Q12: 0<br>A.First<br>B.second<br>C.fourth<br>D.sixth
Q29: Which of the following statements is true
Q79: Figure: Production Possibility Frontier Curve for Tealand<br>
Q86: Which of the following rays consist of
Q126: Which of the following particles is emitted
Q175: The opportunity cost of production:<br>A.is the price
Q395: Figure and Table: The Changing Slope of
Q399: (Table: Optimal Choice of Milk and Honey)