Below is a diagram representing a solvent A(l) in a 1-L beaker, and a solute X dissolved in the solvent. Solvent A has a density of 0.8 g/mL, and a molar mass of 40 g/mol. Solute X has a molar mass of 30 g/mol. Each circle of X represents 1 mol of X. Assume that the solute addition does not significantly change the volume of liquid in the beaker. 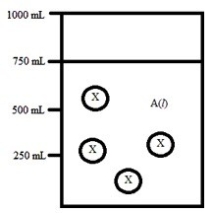 What is the mole fraction of the solute X in this solution?
What is the mole fraction of the solute X in this solution?
Definitions:
Knowledge Repository
A centralized system or database designed to store, manage, and disseminate knowledge and information for easy retrieval and use.
Fact-check
The process of verifying facts and assertions in text, media, or statements to ensure accuracy and prevent misinformation.
Cyberspace
A virtual environment in which communication over computer networks occurs.
Algorithms
Rules that specify operations to find trends in data, and can learn from patterns, as well as make decisions and predict the future.
Q10: Carbon uses _ hybrid orbitals in ClCN.<br>A)
Q17: What is the molar mass of toluene
Q18: The segment <img src="https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB8482/.jpg" alt="The segment
Q30: Ceramics are usually formed by melting and
Q78: How many grams of carbon dioxide are
Q82: Is a bimolecular reaction necessarily second-order? Is
Q102: The rate law for the reaction 3A
Q112: A reactant R is being consumed in
Q119: What is the percent CsCl by mass
Q137: Below is a diagram representing two chambers