Use the following information to answer the question.
Canadian and Swiss researchers wanted to know if the diversity of arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi (AMF) was important to the productivity of grasslands (M.G.A. van der Heijden, J. N. Klironomos, M. Ursic, P. Moutoglis, R. Streitwolf-Engel, T. Boler, A. Wiemken, and I. R. Sanders. 1998. Mycorrhizal fungal diversity determines plant biodiversity, ecosystem variability, and productivity. Nature 396:69-72) . Specifically, they wanted to know if it mattered which specific AMF species were present, or just that some type of AMF was present. They grew various plants in combination with one of four AMF species (A, B, C, and D) , no AMF species (O) , or all four AMF species together (A + B + C + D) ; and they measured plant growth under each set of conditions. All plant species were grown in each plot, so they always competed with each other with the only difference being which AMF species were present.
On the graphs, the x-axis labels indicate the number and identity of AMF species (bar 0 = no fungi; bars A - D = individual AMF species; bar A + B + C + D = all AMF species together) . The y-axis indicates the amount (grams) of plant biomass for the species shown in italics above each graph. Graph e is the total biomass (grams) of all 11 plant species combined; graph f is the biomass of Bromus erectus plants only, separated from the total.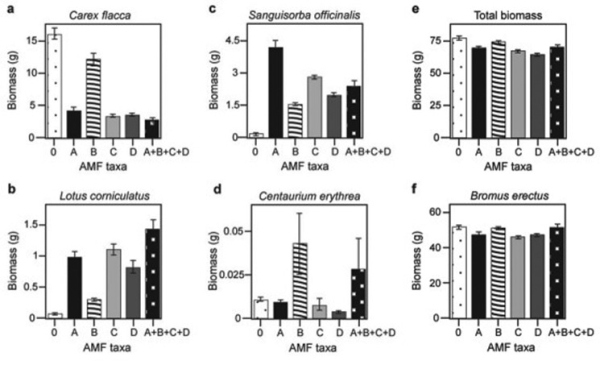
What is the most likely explanation for the observation that total biomass (graph e) does not vary with AMF diversity?
Definitions:
Q2: The first genetic material on Earth was
Q19: In the oceans on either side of
Q23: Which of the following plants are annuals?<br>A)
Q23: Use the information to answer the following
Q36: What is the most accurate method used
Q46: Some molecular data place the giant panda
Q56: In the pressure-flow mechanism, loading of sucrose
Q63: Many parasitic members of the excavates lack
Q80: Use the following information to answer the
Q81: If bryophytes do not have vascular tissue,