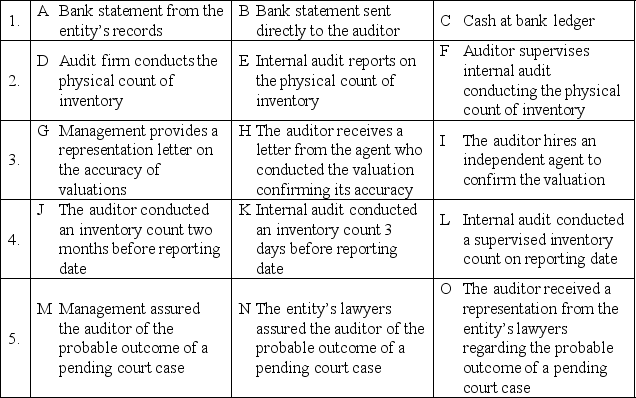
For each of the following combinations of audit evidence, rank the items in terms of their reliability:
Definitions:
Tertiary Prevention
Efforts to reduce the impact of an ongoing illness or injury that has lasting effects.
Primary Prevention
A type of prevention practised prior to the biological origin of the disease (for example, immunization). See also secondary prevention and tertiary prevention.
Secondary Prevention
A type of prevention practised after the disease is identified but before it has caused suffering and disability (for example, the control of blood sugar early in the course of diabetes to prevent systemic damage). See also primary prevention and tertiary prevention.
Tertiary Programs
Educational or treatment programs designed to offer specialized and advanced learning or care options, often after primary and secondary options have been exhausted.
Q1: Discuss some methods a small business can
Q2: As inflation increases, the impact of the
Q2: What does it mean when a lender
Q8: How can a small business owner prevent
Q10: Explain the basic idea behind the TARP
Q16: The auditor is performing substantive procedures several
Q17: Which of the following is not normally
Q31: Under ASA 200/ IAS 200 the primary
Q32: Control activities are detailed policies and procedures
Q40: Which of these would not be a