TABLE 10-14
The use of preservatives by food processors has become a controversial issue. Suppose two preservatives are extensively tested and determined safe for use in meats. A processor wants to compare the preservatives for their effects on retarding spoilage. Suppose 15 cuts of fresh meat are treated with preservative I and 15 are treated with preservative II, and the number of hours until spoilage begins is recorded for each of the 30 cuts of meat. The results are summarized in the table below.
Preservative I Preservative II
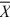 I = 106.4 hours
I = 106.4 hours 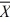 II= 96.54 hours
II= 96.54 hours
SI = 10.3 hours SII = 13.4 hours
-Referring to Table 10-14, state the null and alternative hypotheses for testing if the population variances differ for preservatives I and II.
Definitions:
Weight Losses
Weight losses refer to the amount of weight that an individual or a group loses over a period, often measured in studies related to diet, fitness, or health interventions.
Lubricants
Substances applied to surfaces to reduce friction between them, thereby minimizing heat generation and wear during movement.
P-value Approach
A method in statistical hypothesis testing that determines the smallest level of significance at which the null hypothesis can be rejected, based on the observed data.
Null Hypothesis
A statement of no effect or no difference, used as a starting point for statistical hypothesis testing.
Q3: Referring to Table 12-3, suppose the director
Q36: Referring to Table 10-15, suppose α =
Q43: Referring to Table 12-9, the p-value of
Q102: Referring to Table 9-8, the largest level
Q120: If a test of hypothesis has a
Q201: Referring to Table 12-8, the interpretation of
Q211: Referring to Table 10-12, the p-value of
Q255: Referring to Table 10-6, the p-value for
Q262: Referring to Table 10-11, the same decision
Q276: Referring to Table 13-4, at the 0.01