The following information relates to Questions 1-6
katrina black, portfolio manager at Coral bond Management, ltd., is conducting a training session with alex Sun, a junior analyst in the fixed income department. black wants to ex-plain to Sun the arbitrage-free valuation framework used by the firm. black presents Sun with exhibit 1, showing a fictitious bond being traded on three exchanges, and asks Sun to identify the arbitrage opportunity of the bond. Sun agrees to ignore transaction costs in his analysis.exhibit 1 Three-Year, €100 par, 3.00% Coupon, annual-Pay option-Free bond
black shows Sun some exhibits that were part of a recent presentation. exhibit 3 presents most of the data of a binomial lognormal interest rate tree fit to the yield curve shown in ex-hibit 2. exhibit 4 presents most of the data of the implied values for a four-year, option-free, annual-pay bond with a 2.5% coupon based on the information in exhibit 3.exhibit 2 Yield to Maturity Par rates for one-, two-, and Three-Year annual-Pay option-Free bonds
exhibit 3 binomial interest rate tree Fit to the Yield Curve (Volatility = 10%)
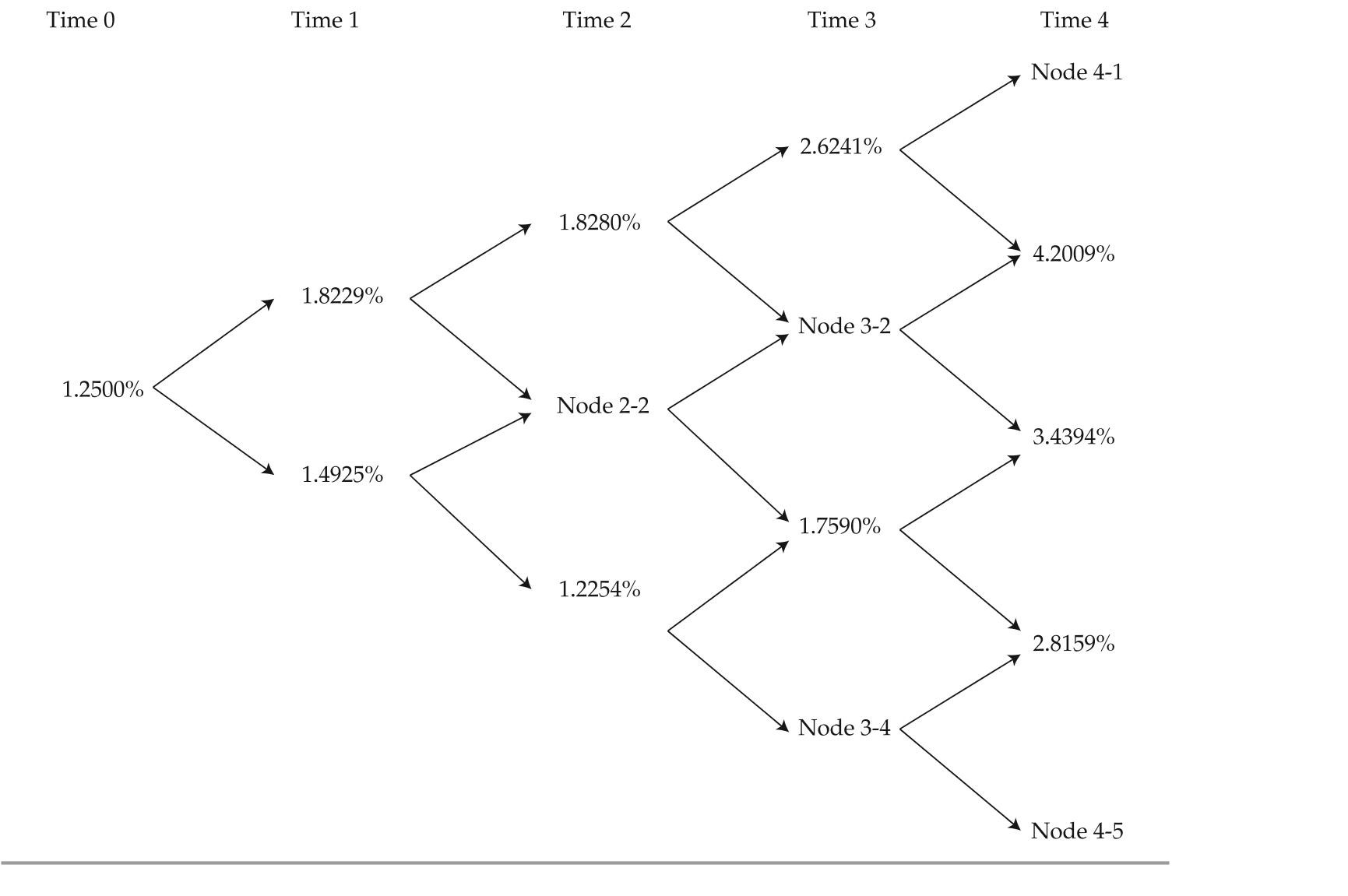 exhibit 4 implied Values (in euros) for a 2.5%, Four-Year, option-Free, annual-Pay bond based on exhibit 3
exhibit 4 implied Values (in euros) for a 2.5%, Four-Year, option-Free, annual-Pay bond based on exhibit 3
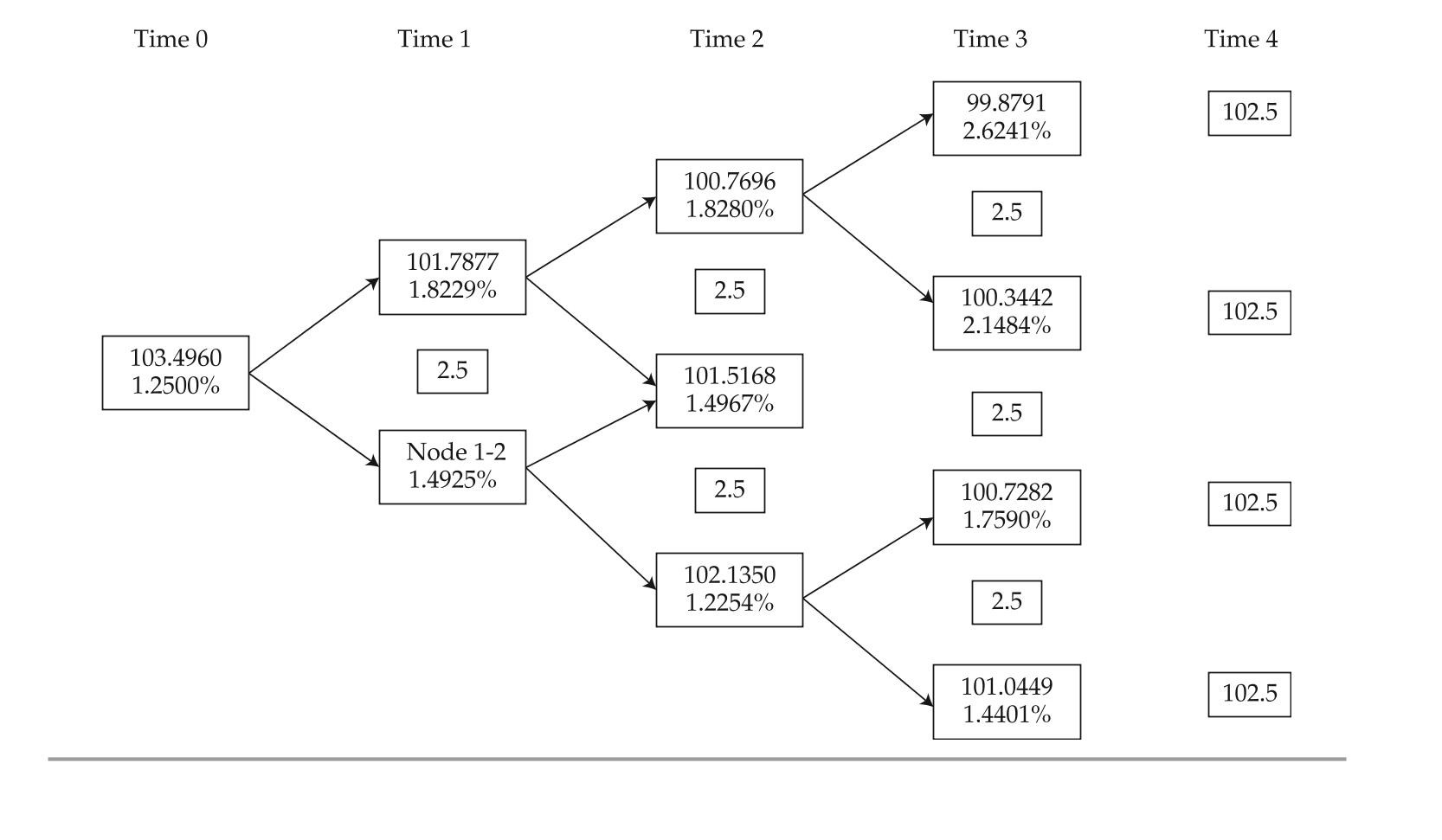 black asks about the missing data in exhibits 3 and 4 and directs Sun to complete the following tasks related to those exhibits:
black asks about the missing data in exhibits 3 and 4 and directs Sun to complete the following tasks related to those exhibits:
task 1 test that the binomial interest tree has been properly calibrated to be arbitrage-free.
task 2 Develop a spreadsheet model to calculate pathwise valuations. to test the ac-curacy of the spreadsheet, use the data in exhibit 3 and calculate the value of the bond if it takes a path of lowest rates in Year 1 and Year 2 and the second lowest rate in Year 3.
task 3 identify a type of bond where the Monte Carlo calibration method should be used in place of the binomial interest rate method.
task 4 update exhibit 3 to reflect the current volatility, which is now 15%.
-if the assumed volatility is changed as black requested in task 4, the forward rates shown in exhibit 3 will most likely:
Definitions:
Negative Reinforcement
A type of learning where a behavior is strengthened because it is followed by the removal of an unpleasant stimulus.
Positive Reinforcement
A method in behaviorism that involves the addition of a rewarding stimulus following a desired behavior, with the aim of increasing the likelihood of that behavior being repeated.
Aversive Condition
A situation or stimulus that is unpleasant or uncomfortable and which an individual seeks to avoid or escape.
Negative Reinforcement
A behavioral psychology concept where the removal of an undesirable or negative stimulus strengthens a behavior.
Q4: Determine whether the Law of Sines
Q5: A beam with an overhang is
Q6: Three couples of equal magnitude
Q9: david lok has estimated the probability of
Q14: The distinction between investment grade debt and
Q29: The bond's yield-to-worst is closest to:<br>A) 2.88%.<br>B)
Q75: Two curves are said to be
Q97: Determine whether <span class="ql-formula" data-value="f"><span
Q101: <span class="ql-formula" data-value="\text { Use a graph
Q125: <span class="ql-formula" data-value="\text { Find the function