The density curve for a continuous random variable is shown below. Use this curve
to find the following probabilities: 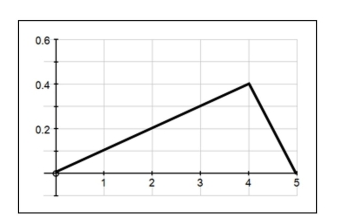
a)
b) P ( 2 < x < 4 )
You may need to use the following area formulas in your calculations:
Area of a rectangle:
Area of a trapezoid:
Area of a right triangle:
Definitions:
AASB 11
Australian Accounting Standard Board's directive concerning the financial reporting of interests in joint arrangements to ensure transparency and comparability.
Alternative Reporting Formats
Refers to various formats a company may use to present its financial statements, outside of the standard formats.
Joint Venture
A business arrangement in which two or more parties agree to pool their resources for the purpose of accomplishing a specific project or business activity.
Joint Operation
An arrangement where two or more parties undertake an economic activity that is subject to joint control, where the parties have rights to the assets and obligations for the liabilities.
Q15: Solve the boundary-value problem, if possible.<br>
Q15: In a study performed by the statistics
Q24: Increasing sample size will eliminate bias in
Q28: Which of the following is not inversely
Q43: What is the probability that the selected
Q44: <span class="ql-formula" data-value="\text { Two events, }
Q65: The sketch of the solid is
Q101: Graph the particular solution and several
Q139: Solve the initial-value problem.<br> <span class="ql-formula"
Q265: Which of these sets of nations consists