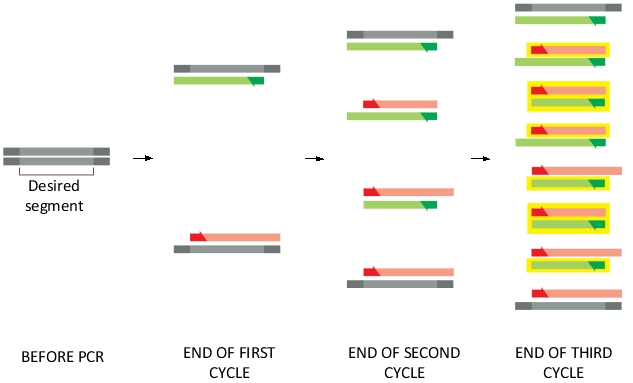
Each cycle of PCR doubles the amount of DNA synthesized in the previous cycle. A pair of primers is used to direct the specific synthesis of a desired DNA segment. The following diagram shows the products of PCR amplification after three cycles. The DNA strands of the desired segment are indicated in yellow boxes in the diagram. As shown, at the end of the third cycle, 8 out of 16 strands have the desired length and are boxed. After four more cycles (i.e. at the end of the seventh cycle), how many strands of DNA are expected to be synthesized? How many of them have the desired length? Write down the two numbers and separate them with a comma, e.g. 16,8.
Definitions:
Beta
A measure of the volatility, or systematic risk, of a security or a portfolio in comparison to the market as a whole.
Technical Indicator
A mathematical calculation based on historical price, volume, or open interest information that aims to forecast financial market direction.
Variance Inflation Factor
A measure used in statistics to identify the degree of multicollinearity in a set of regression variables.
Multicollinearity
A statistical phenomenon in which predictor variables in a multiple regression model are highly correlated, potentially diminishing the reliability of the estimates.
Q2: Which of the following is NOT a
Q10: Indicate true (T) and false (F) statements
Q19: What is the amino acid sequence of
Q26: Two segments (S1 and S2) in a
Q26: Macromolecules in the cell can be made
Q38: In the schematic drawing of the structure
Q42: The eukaryotic chromosomes are organized inside the
Q50: Your friend who is studying the sequence
Q70: Indicate whether each of the following manipulations
Q95: The following graph shows the change in