In the following graphs, the cellular response, as measured in real time by the concentration of a certain active effector protein, is plotted over time for five cell types (A to E) that are treated with three different concentrations of a signal molecule. During the time period indicated by the horizontal gray bar, the signal molecule is present in the culture media at a concentration of 1 nM (dotted curve), 5 nM (gray curve), or 25 nM (solid curve). Answer the following question(s) based on these graphs.
-Which of the cell types A to E shows the widest dynamic range of signal concentration?
A)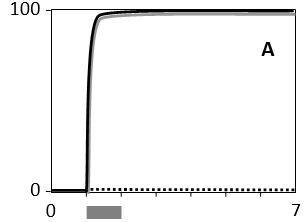
B)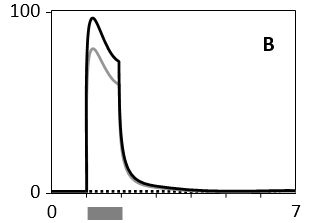
C)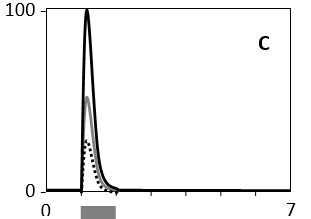
D)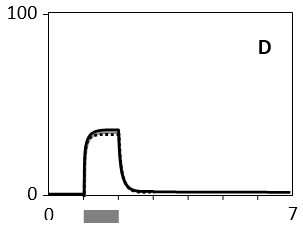
E)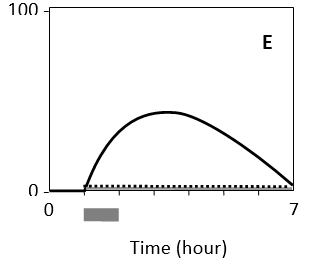
Definitions:
Unstructured Data
Data that does not follow a specified format or structure, making it difficult to collect, process, and analyze using conventional methods.
Relational Database
A database structured to recognize relations among stored items of information according to a relational model of data.
Big Data
Large and complex data sets that are difficult to process using traditional data processing applications, often requiring advanced analytics and storage solutions.
Traditional DBMS
Database management systems that support a model, typically the relational model, which uses a structured query language (SQL) for defining and manipulating data.
Q4: In actively respiring mitochondria, where in the
Q10: In neurons, the synaptotagmin-1 protein is localized
Q11: The motion of lipid molecules in a
Q18: In the following diagram showing five parallel
Q26: Two segments (S1 and S2) in a
Q46: Which of the following groups of proteins
Q47: Resveratrol is a natural compound found in
Q64: In a bacterium that is normally cylindrical
Q73: You have carried out a genetic screen
Q74: Everything else being equal, if the mean