Use the percentage method of withholding to find the federal withholding tax, a 6.2% FICA rate to find the FICA tax, and
1.45% to find the Medicare tax. Then find the net pay for the employee. Assume that the employee has not earned over
$115,000 so far this year. 
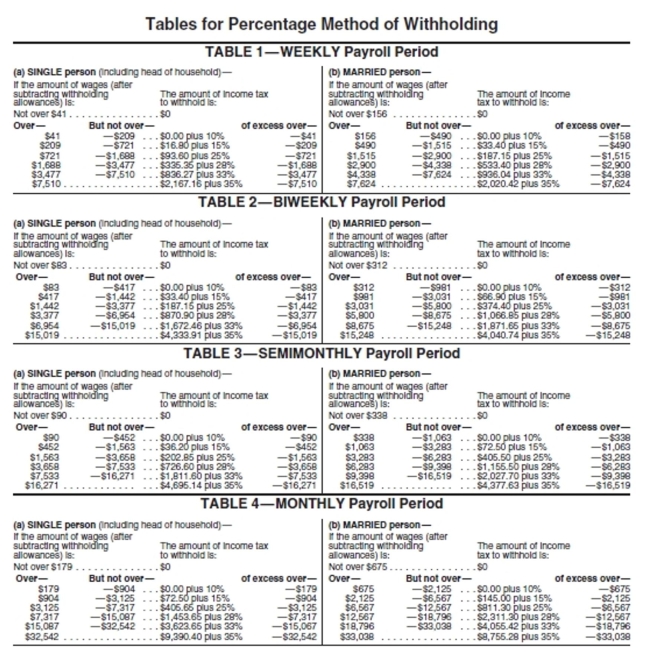
-Erika Du Mesnil has gross earnings of $7914.27 semimonthly. She is married and has 4 withholding allowances.
Definitions:
WEIRD Participants
Refers to subjects of behavioral science research who are predominantly from Western, Educated, Industrialized, Rich, and Democratic societies, leading to questions regarding the universality of study results.
Measures of Construct
Refers to tools or methods used to assess the presence and strength of theoretical constructs.
Measurement Error
The difference between the observed value and the true value of a variable, often arising from inaccuracies in data collection or processing.
Valid
Refers to the extent to which a concept, conclusion, or measurement is well-founded and corresponds accurately to the real world.
Q3: Explain in your own words what a
Q5: Use the graph to find the slope,
Q14: Sven can type 48 words per minute.
Q17: $46,228 at 7.4% for 23 months<br>A)$6,611.77; $52,839.77<br>B)$6,841.74;
Q30: What is a simple discount note? Explain
Q36: Describe the difference between a trade discount
Q38: In your own words, explain how you
Q57: <img src="https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB8285/.jpg" alt=" A)Cost Price: $12.80
Q62: $10,593 at 6.9% for 9 months<br>A)$552.79; $11,145.79<br>B)$548.19;
Q130: <img src="https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB8593/.jpg" alt=" A)