SCENARIO 15-4 The superintendent of a school district wanted to predict the percentage of students passing a sixth-grade proficiency test.She obtained the data on percentage of students passing the proficiency test (% Passing), daily mean of the percentage of students attending class (% Attendance), mean teacher salary in dollars (Salaries), and instructional spending per pupil in dollars (Spending)of 47 schools in the state. Let Y = % Passing as the dependent variable, 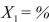 Attendance,
Attendance, 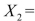 Salaries and
Salaries and 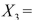 Spending. The coefficient of multiple determination (
Spending. The coefficient of multiple determination ( 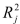 )of each of the 3 predictors with all the other remaining predictors are, respectively, 0.0338, 0.4669, and 0.4743. The output from the best-subset regressions is given below:
)of each of the 3 predictors with all the other remaining predictors are, respectively, 0.0338, 0.4669, and 0.4743. The output from the best-subset regressions is given below: 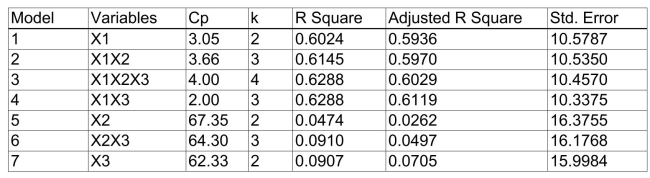 Following is the residual plot for % Attendance:
Following is the residual plot for % Attendance: 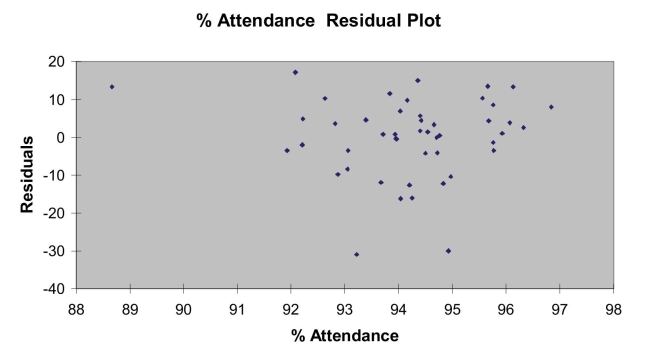 Following is the output of several multiple regression models:
Following is the output of several multiple regression models: 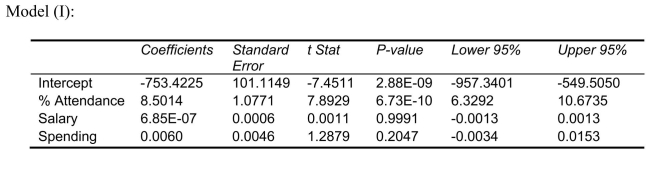
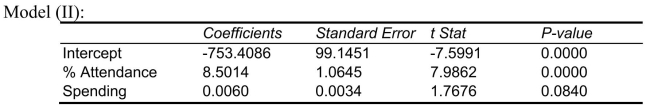
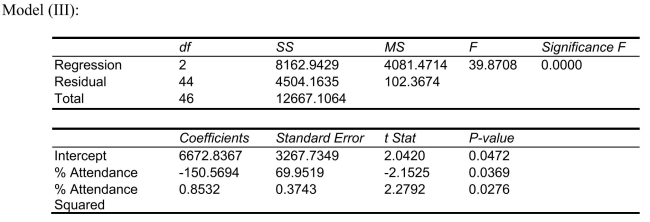
-what is the p-value of the test statistic to determine whether the quadratic effect of daily average of the percentage of students attending class on percentage of students passing the proficiency test is significant at a 5% level of significance?
Definitions:
Proactive Interference
The phenomenon where old memories hinder the recall of newly learned information.
Retroactive Interference
A phenomenon in which newer memories impair the retrieval of older memories stored previously.
Memory Construction
The process of forming and integrating new memories, which involves encoding, storage, and retrieval.
Encoding
The act of turning details into a configuration that allows for storage in memory.
Q13: Due to the amount of the space
Q33: Referring to Scenario 17-3, what is the
Q51: Referring to Scenario 14-18, the null hypothesis
Q97: Referring to Scenario 14-15, which of the
Q108: At a meeting of information systems officers
Q175: Referring to Scenario 18-3, the analyst wants
Q183: Referring to Scenario 18-1, what minimum annual
Q189: Referring to Scenario 14-7, the value of
Q292: Referring to Scenario 18-8, which of the
Q334: Referring to Scenario 14-18, there is not