SCENARIO 15-4 The superintendent of a school district wanted to predict the percentage of students passing a sixth-grade proficiency test.She obtained the data on percentage of students passing the proficiency test (% Passing), daily mean of the percentage of students attending class (% Attendance), mean teacher salary in dollars (Salaries), and instructional spending per pupil in dollars (Spending)of 47 schools in the state. Let Y = % Passing as the dependent variable, 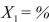 Attendance,
Attendance, 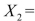 Salaries and
Salaries and 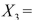 Spending. The coefficient of multiple determination (
Spending. The coefficient of multiple determination ( 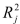 )of each of the 3 predictors with all the other remaining predictors are, respectively, 0.0338, 0.4669, and 0.4743. The output from the best-subset regressions is given below:
)of each of the 3 predictors with all the other remaining predictors are, respectively, 0.0338, 0.4669, and 0.4743. The output from the best-subset regressions is given below: 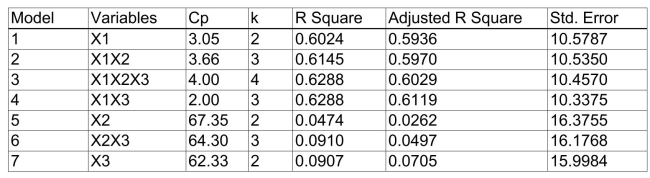 Following is the residual plot for % Attendance:
Following is the residual plot for % Attendance: 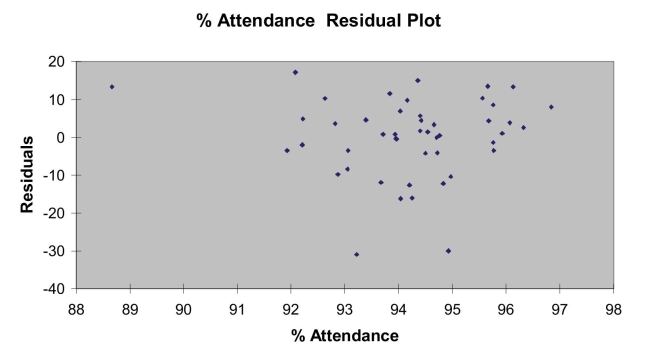 Following is the output of several multiple regression models:
Following is the output of several multiple regression models: 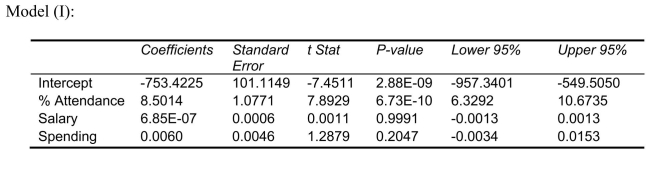
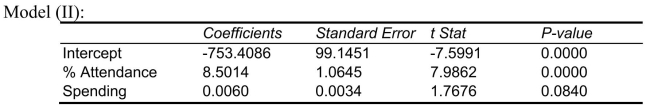
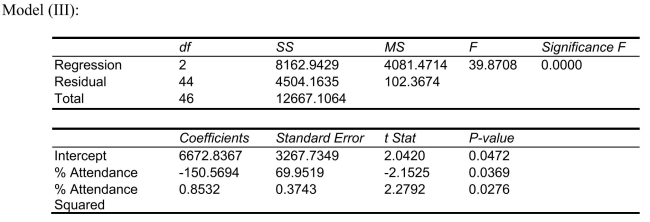
-Referring to Scenario 15-4, the quadratic effect of daily average of the percentage of students attending class on percentage of students passing the proficiency test is not significant at a 5% level of significance.
Definitions:
Unconditioned Stimulus
In classical conditioning, a stimulus that naturally and automatically triggers a response without any prior learning.
Conditioned Stimulus
A previously neutral stimulus that, after becoming associated with an unconditioned stimulus, eventually comes to trigger a conditioned response.
Acquisition
The initial learning of the connection between the unconditioned stimulus and the conditioned stimulus when these two stimuli are paired.
Association
A connection or linkage between thoughts, ideas, feelings, or memories, influenced by experiences or learning.
Q24: Referring to Scenario 17-7, the "complete" method
Q26: If a time series does not exhibit
Q33: Referring to Scenario 16-12, using the regression
Q78: Referring to Scenario 18-1, at the 0.01
Q81: Referring to Scenario 14-19, what are the
Q122: Referring to Scenario 14-17, which of the
Q124: Referring to Scenario 14-16, which of the
Q144: A buyer for a manufacturing plant suspects
Q170: Referring to Scenario 14-19, what is the
Q274: A researcher randomly sampled 30 graduates, 18