Table 10-5
The following table shows the marginal costs for each of four firms (A, B, C, and D) to eliminate units of pollution from their production processes. For example, for Firm A to eliminate one unit of pollution, it would cost $54, and for Firm A to eliminate a second unit of pollution it would cost an additional $67. 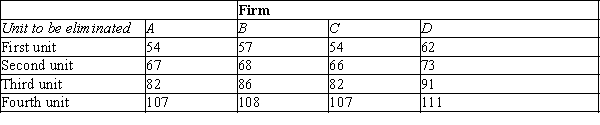
-Refer to Table 10-5. Suppose the government wants to reduce pollution from 16 units to 8 units and auctions off 8 pollution permits to achieve this goal. Which of the following is a likely auction price of the permits?
Definitions:
Hofmann Elimination
A chemical reaction where an amine is treated with an excess of a halogen compound to yield an alkene.
E2 Pathway
A type of bimolecular elimination reaction mechanism where a substrate undergoes deprotonation by a base, leading to the formation of a double bond and the loss of a leaving group in a single step.
E1
A type of unimolecular elimination reaction where the rate determining step involves the removal of a leaving group, forming a carbocation intermediate.
Major Organic Product
In organic chemistry reactions, it is the main product formed, characterized by being present in the greatest amount among products resulting from the conversion of reactants.
Q32: Refer to Figure 9-17.The deadweight loss caused
Q33: Refer to Table 11-3.If the marginal cost
Q64: Suppose that flu shots create a positive
Q85: Pollution is a negative externality,but it is
Q102: Suppose France imposes a tariff on wine
Q211: Technology spillover is one type of<br>A) negative
Q221: Which of the following is an approach
Q241: The value and cost of goods are
Q343: In recent years,which countries have taken a
Q344: Refer to Figure 11-1.Cable TV is an