Instruction 2-1 Unless instructed otherwise, compute hourly rate and overtime rates as follows:
1. Carry the hourly rate and the overtime rate to 3 decimal places and then round off to 2 decimal places (round the hourly rate to 2 decimal places before multiplying by one and one-half to determine the overtime rate).
2. If the third decimal place is 5 or more, round to the next higher cent.
3. If the third decimal place is less than 5, drop the third decimal place.
Also, use the minimum hourly wage of $7.25 in solving these problems and all that follow.
Refer to Instruction 2-1 . Gates is paid a semimonthly salary of $900.00. Overtime is paid for hours beyond 40 in
each workweek. One week, Gates works 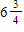 hours overtime. Gates' pay for this semimonthly pay period is _____.
hours overtime. Gates' pay for this semimonthly pay period is _____.
Definitions:
Federal Reporter
A collection of case law from federal courts of appeal, used as references for legal precedent.
Citation
A reference to a source of legal authority, such as statutes, cases, or regulations, or the act of issuing a notice of violation to an individual.
Sixth Circuit
Refers to a federal judicial circuit in the United States, covering portions of Michigan, Ohio, Kentucky, and Tennessee, known for its appellate jurisdiction.
Docket Number
An identification number assigned by a court to a case, used to track and locate court records and proceedings related to that case.
Q1: E-SIGN and UETA do not require consent
Q5: A seller may resell goods as a
Q9: A warranty created by exclusion is<br>A)limited.<br>B)full.<br>C)incomplete.<br>D)unconscionable.
Q20: Instruction 5-1 <br>Use the net FUTA tax
Q21: Unions and employment agencies are excluded from
Q22: The Fair Labor Standards Act is commonly
Q31: Verifying the history or treatment of a
Q50: Which of the following is used to
Q59: A college may employ its own full-time
Q99: Which of the following statements about Andy