The diagram below is a time-concentration curve for the reaction CO₂ (g) C (s) + O₂(g) . What is the average rate at which CO₂ (g) disappears over the first 25 minutes of the reaction?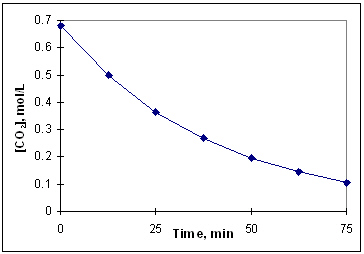
Definitions:
Carbocation Intermediate
A positively charged ion (cation) characterized by the presence of a carbon atom having only six electrons in its valence shell, often occurring in organic reactions.
Resonance Contributors
Structures that depict the delocalization of electrons within a molecule, showing different possible configurations without changing the placement of atoms.
Major Products
In chemical reactions, the major products are the substances produced in the greatest amount, determined by the reaction conditions and mechanism.
Structures
The arrangement of and relations between the parts or elements of something complex, such as a molecule’s geometric configuration.
Q16: Which of the following quantities is least
Q44: At 1073 K, the pressure of CO₂
Q69: How many grams of Na<sub>2</sub>CO<sub>3</sub> are required
Q79: A solution of KOH is found to
Q114: Which salt(s) listed below form(s) an acidic
Q124: For the reaction 2 H₂ O (g)
Q141: Which of the following acids is considered
Q152: What is the pH of 0.0040 M
Q154: Which of the following reactions is product
Q185: Three hundred milliliters (300 mL) of 2.50