When Service A receives a message from Service Consumer A(1) ,the message is processed by Component A. This component first invokes Component B (2) , which uses values from the message to query Database A in order to retrieve additional data. Component B then returns the additional data to Component A. Component A then invokes Component C (3) , which interacts with the API of a legacy system to retrieve a new data value. Component C then returns the data value back to Component A. Next, Component A sends some of the data it has accumulated to Component D (4) , which writes the data to a text file that is placed in a specific folder. Component D then waits until this file is imported into a different system via a regularly scheduled batch import. Upon completion of the import, Component D returns a success or failure code back to Component A. Component A finally sends a response to Service Consumer A (5) containing all of the data collected so far and Service Consumer A writes all of the data to Database B (6) . Components A, B, C. and D belong to the Service A service architecture. Database A, the legacy system, and the file folders are shared resources within the IT enterprise. 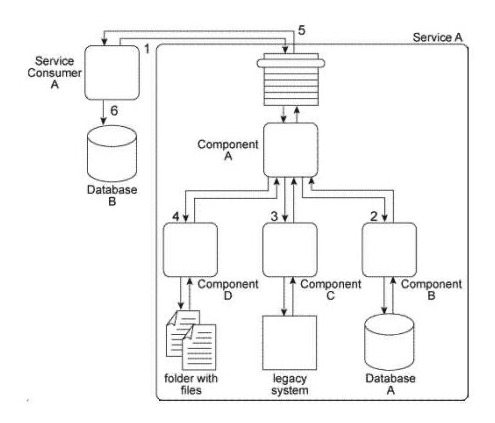 Service A is a task service that completes an entire business task on its own without having to compose other services. However, you have received many complaints about the reliability of Service A . Specifically, it has three problems. First, when Component B accesses Database A, it may not receive a response for several minutes when the database is being accessed by other applications in the IT enterprise. Secondly, the legacy system accessed by Component C frequently crashes and therefore becomes unavailable for extended periods of time. Third, for Component D to respond to Component A, it must first wait for the batch import of the files to occur. This can take several minutes during which Service Consumer A remains stateful and consumes excessive memory. What steps can be taken to address these three problems?
Service A is a task service that completes an entire business task on its own without having to compose other services. However, you have received many complaints about the reliability of Service A . Specifically, it has three problems. First, when Component B accesses Database A, it may not receive a response for several minutes when the database is being accessed by other applications in the IT enterprise. Secondly, the legacy system accessed by Component C frequently crashes and therefore becomes unavailable for extended periods of time. Third, for Component D to respond to Component A, it must first wait for the batch import of the files to occur. This can take several minutes during which Service Consumer A remains stateful and consumes excessive memory. What steps can be taken to address these three problems?
Definitions:
Fast Adaptive Mode
High-speed processing algorithms; Allison uses this term to describe an operating condition in which large changes are made to initial shift conditions to adjust for major system tolerances such as solenoid-to-solenoid, main pressure, and clutch-to-clutch variations. A new or newly rebuilt transmission should be programmed to operate in fast adaptive mode.
Close-ratio Gearing
A transmission design where the gear ratios are closer together, allowing the engine to operate more consistently near its optimal RPM for performance.
Standard Gear Ratios
The predefined set of gear ratios used in transmissions to optimize vehicle performance and fuel efficiency under normal driving conditions.
Latching Solenoid
A solenoid device that can hold its position (engaged or disengaged) without needing continuous electrical power, a reemphasis on its function for maintaining states.
Q3: Which of the following statements about reviews
Q27: A storage subsystems Web browser management interface
Q27: IT management wants to know how they
Q41: The following statement describes the relationship between
Q47: A _ establishes a common access point
Q53: What are two supported ways to integrate
Q58: Listening is the most frequently used form
Q95: The ROI (return on investment) potential of
Q197: What may leave more risk than a
Q200: _ is an agreement between two counterparties