Figure 1:
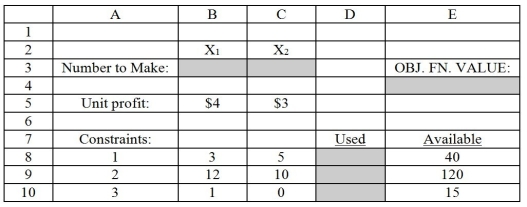
Figure 1 demonstrates an Excel spreadsheet that is used to model the following linear programming problem:
Note: Cells B3 and C3 are the designated cells for the optimal values of X₁ and X₂,respectively,while cell E4 is the designated cell for the objective function value.Cells D8:D10 designate the left-hand side of the constraints.
-Refer to Figure 1.What formula should be entered in cell E4 to compute total profitability?
Definitions:
Predictive
Relating to the ability to foretell or forecast future events or behaviors based on current data or past experiences.
Negatively Correlated
A relationship between two variables in which one variable increases as the other decreases.
Cross-Cultural Studies
Research that compares cultural norms, values, and practices across different societies or ethnic groups.
Less Technologically Advanced
Refers to entities or societies that have a lower level of technology, equipment, and modern conveniences compared to others.
Q11: Sensitivity analysis is analogous to postoptimality analysis
Q15: Which of the following external recruitment techniques
Q18: _items have to be included as part
Q22: Discuss the characteristics of a multicultural organization.
Q23: Refer to Scenario 13.1.Refer to Scenario 13.1.The
Q27: Write a short note on ways to
Q31: The projective technique involves showing individuals abstract
Q33: Which of the following theories of motivation
Q40: Refer to the table above.Use a linear
Q49: What distribution is appropriate for simulating the