Now imagine that the votes for each party shown in Table 2 are the same, but that they are for a district where 10 candidates are elected using a highest average system to allocate seats. This means that the votes parties receive are divided by a series of numbers to give quotients. This country uses the d'Hondt method (the divisors are 1, 2, 3, 4, . . . ) . Seats are allocated to the party with the largest quotient, then the second largest, then the third largest . . . until all of the seats have been allocated. In Table 3, the quotients have already been calculated for you and are shown in italics. Use Table 3 to answer Questions .
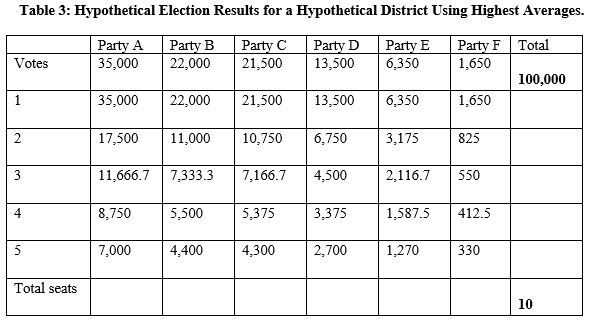
-If the election results shown in Table 3, above, were for a district with a magnitude of 1 and the alternative vote rule was used, what would the outcome be?
Definitions:
Comparative Advantage
The ability of an individual or group to produce a good or service at a lower opportunity cost than others, leading to more efficient trade possibilities.
Production Possibility
A graph showing the highest possible production levels of two items, using a specific combination of resources and various factors.
Opportunity Costs
Making a choice results in the loss of potential profit that could have been earned from choosing differently.
Increasing Opportunity
In economic terms, refers to the increasing cost associated with producing additional units of a good, implying that producing more of one good requires sacrificing increasingly larger amounts of another good.
Q1: The purpose of rehabilitation is to:<br>A) change
Q5: Which of the following is not a
Q9: Where should you store your emergency kit?<br>A)In
Q13: Define reintegrative shaming. How does it differ
Q14: As the number of individuals and/or the
Q15: In a representative democracy, the series of
Q16: Which of the following statements explain why
Q17: According to reentry theory, which of the
Q18: Describe, in your own words, each of
Q18: Mandates are not particularly important in consensus