Figure 13-12
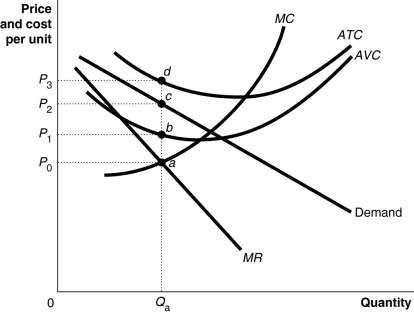
Figure 13-12 shows short-run cost and demand curves for a monopolistically competitive firm in the market for designer watches.
-Refer to Figure 13-12.If the diagram represents a typical firm in the designer watch market, what is likely to happen in the long run?
Definitions:
Receivables Period
The amount of time it takes for a company to collect payments owed by its customers after a sale has been made.
Selling Price
The amount of money charged for a product or service, or the sum obtained from the sale of an asset.
Receivables
Money owed to a company by customers for goods or services that have been delivered or used but not yet paid for.
Ending Cash Balance
The amount of cash a company has available at the end of a financial period.
Q13: For a firm in a perfectly competitive
Q49: Refer to Figure 11-18.Starting from point E,
Q80: Refer to Figure 12-16.Which panel best represents
Q99: A reason why there is more competition
Q113: Refer to Figure 12-2.What happens if the
Q142: A monopolistically competitive firm that is profitable
Q145: A characteristic found only in oligopolies is<br>A)break-even
Q188: A major difference between monopolistic competition and
Q199: Consider the following characteristics:<br>A.a market structure with
Q268: Refer to Table 13-3.If this firm continues