The following questions refer to Figure 27.1 below, which is the same as Figure 27.10 in the textbook.
In this 8-year experiment, 12 populations of E. coli, each begun from a single cell, were grown in low-glucose conditions for 20,000 generations. Each culture was introduced to fresh growth medium every 24 hours. Occasionally, samples were removed from the populations, and their fitness in low-glucose conditions was tested against that of members sampled from the ancestral (common ancestor) E. coli population.
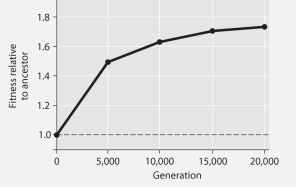
Figure 27.1
-If the experimental population of E. coli lacks an F factor or F plasmid, and if bacteriophage are excluded from the bacterial cultures, then which of these is a means by which beneficial mutations might be transmitted horizontally to other E. coli cells?
Definitions:
Alcoholism
A chronic condition involving an uncontrollable desire to drink alcohol despite the negative impact it has on one's health, social life, and responsibilities.
Genetic Vulnerability
The predisposition of certain individuals to diseases or conditions due to specific genetic factors inherited from their parents.
Disease
A condition that impairs normal bodily functions and is often characterized by specific signs and symptoms.
Vital Functions
Essential bodily operations necessary for maintaining life, such as respiration, circulation, and digestion.
Q1: Why would Gleevec most probably cause remission
Q5: What does the field often called "evo-devo"
Q6: Which of the following techniques used to
Q12: Suppose a moss evolved an efficient conducting
Q14: Test tube 1 contains<br>A)Paramecium<br>B)Navicula (diatom)<br>C)Pfiesteria (dinoflagellate)<br>D)Entamoeba<br>E)Plasmodium
Q32: A hypothetical mutation in a squirrel population
Q34: In which of these human mycoses should
Q46: You are given an unknown organism to
Q57: Many physicians administer antibiotics to patients at
Q74: In a Hardy-Weinberg population with two alleles,