To evaluate cardiac function, scientists and physicians measure both the pressure and the volume inside the heart. When both pressure and volume data are plotted on the same graph, the resulting graph is called a pressure-volume loop. To create a pressure-volume loop, a catheter (a thin tube) is inserted into the vessels of the heart, and measurements of both left ventricular pressure and left ventricular volume are taken. The data are plotted on a graph, and cardiac function can then be evaluated from the distribution of the data and the shape of the loop.
The following figure shows a typical left ventricle pressure-volume loop for a healthy young adult. The cardiac cycle proceeds counterclockwise. Each complete turn around the loop (for example, starting at point A and ending back at point A) represents one complete cardiac cycle.
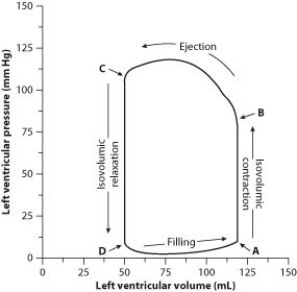
-How much blood is ejected from the left ventricle during one contraction?
Definitions:
B.F. Skinner
An American psychologist and behaviorist known for his work in operant conditioning, emphasizing the role of reinforcement and punishment in shaping behavior.
Mirror Neurons
Neurons that fire both when an individual performs an action and when they observe the same action being performed by another, thought to be fundamental in imitation, empathy, and social understanding.
Active
Engaging or ready to engage in physically energetic pursuits.
Mirror Neurons
Neurons that fire both when an individual acts and when the individual observes the same action performed by another, thought to play a role in learning and empathy.
Q22: The main function of the rough endoplasmic
Q23: The four most common elements in living
Q27: What do you predict that group 3
Q32: Which of the following processes involves heat
Q37: The ability to stain protein molecules with
Q43: Which of the following is dependent on
Q61: Whether there is a net flow of
Q71: After counting query hits,how would you go
Q80: You should always use T-Lists for lists
Q91: In a Reports Builder template the _