Dr. Elder was interested in the way people recognize objects as members of categories. For example, what makes us recognize a dog as being a dog and not a cat? More specifically, he was curious as to whether people think about categories in a more complex way if they contemplate an "opposite" category first. For example, does a person think differently about the category of "southern" if they first think about the category of "northern"? He is also curious as to whether people categorize differently if they are exposed to category members compared with generating category members. Dr. Elder has four groups of participants (with 30 people in each group) . In Group A, participants were told to cut out pictures of dogs and cats from magazines. In Group B, participants were told to cut out pictures of just dogs from magazines. In Group C, participants were told to draw pictures of cats and dogs. In Group D, participants were told to draw pictures of just dogs. After doing this for 30 minutes, participants in all groups were asked to list the attributes that define the "dog" category. Having a higher number of attributes listed was considered to be an indication of thinking about the category in a more complex way. The results of his study are below.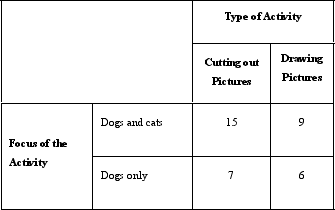
Which of the following reasons is the most likely reason Dr. Elder conducted a factorial design?
Definitions:
Negligent Act
An action or failure to act in a situation where a person has a duty to exercise reasonable care, resulting in harm to another party.
Proportionate Negligence
A legal doctrine that allocates damage recovery based on the degree of fault or negligence contributed by each party involved in an incident.
Liability for Injuries
The legal responsibility to compensate for physical harm or injury caused to another person.
Duty of Care
A legal obligation imposed on individuals and organizations to adhere to a standard of reasonable care while performing any acts that could foreseeably harm others.
Q2: Establishing construct validity would probably be most
Q6: Synergistic effects result when two drugs administered
Q9: State the three types of factorial designs.
Q9: What is not true about ADHD?<br>A)only affects
Q16: opioid antagonists
Q31: A simple difference is also called:<br>A)a factorial
Q39: Why are convergent and discriminant validity often
Q40: If a study uses an unrepresentative sample,
Q52: Which of the following is the most
Q53: Dr. Gavin is conducting a 2 ×