The figure given below shows the aggregate demand and supply curves of a perfectly competitive market. Figure 9.7 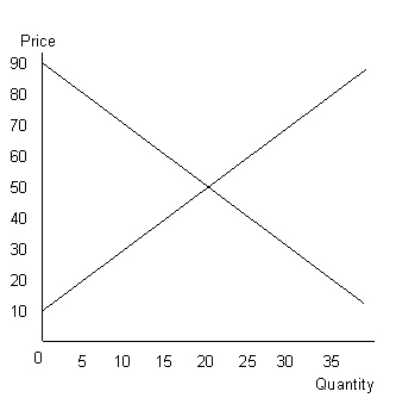
- Refer to Figure 9.7 and calculate the producer surplus.
Definitions:
Failing to Reject
In hypothesis testing, it is the scenario where there isn’t enough evidence to reject the null hypothesis.
Null Hypothesis
A statement of no effect or no difference, serving as the default assumption to be tested against experimental evidence.
P-value
The probability of observing test results at least as extreme as the results actually observed, under the assumption that the null hypothesis is correct.
Level of Significance
The probability of making a Type I error in hypothesis testing, serving as a critical value for deciding whether to reject the null hypothesis.
Q23: According to Figure 9.6,an upward shift of
Q28: In Figure 6.3,the consumer is in equilibrium
Q37: Refer to Table 6.3.Which of the following
Q40: Using Figure 7.1 determine the average
Q58: Compared with a perfectly competitive firm in
Q69: Fixed costs are costs paid for:<br>A)plant,equipment,and land
Q80: Refer to Table 8.3.The economic profit of
Q81: If the average total cost of producing
Q88: Why do the perfectly competitive firms earn
Q89: In long-run equilibrium,the monopolistically competitive firm:<br>A)will break