The figure given below shows the aggregate demand and supply curves of a perfectly competitive market.Figure 10.7
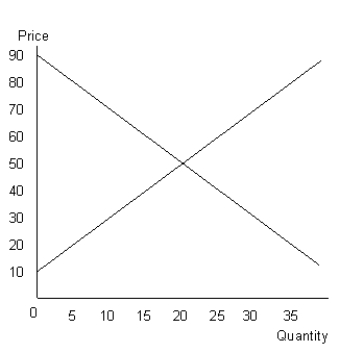
-In the short-run, a perfectly competitive firm can earn normal profits or above normal profit but it cannot incur losses.
Definitions:
Grocery Stores
Retail stores specializing in the sale of food and household items.
Enterprise Value
A measure of a company's total value, calculated as market capitalization plus debt, minority interest, and preferred shares, minus total cash and cash equivalents.
Market Cap
The total market value of a company's outstanding shares of stock, calculated by multiplying the stock's current market price by the total number of shares.
EV/EBITDA Ratio
A valuation metric comparing a company's enterprise value to its earnings before interest, taxes, depreciation, and amortization, highlighting company profitability.
Q10: Which of the following are the three
Q20: When average total cost is minimum,it is:<br>A)equal
Q27: Under perfect competition,the per unit revenue of
Q27: Wikipedia and other projects utilizing wiki technology,represent
Q34: Why does a efficiency loss arise under
Q50: Entry of new firms to the industry
Q68: For a farmer,the long run would be
Q75: When the people creating an externality are
Q105: Buyers who are persuaded to take a
Q130: Supply curves applicable to shorter periods of