Figure 9.1 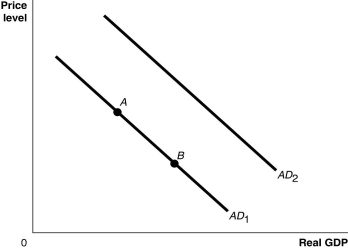 Alt text for Figure 9.1: In figure 9.1, a graph comparing real GDP and price level.
Alt text for Figure 9.1: In figure 9.1, a graph comparing real GDP and price level.
Long description for Figure 9.1: The x-axis is labelled, real GDP, and the y-axis is labelled, price level, with 0 at the vertex.Line AD1 begins in the top left corner and slopes down to the bottom center.Line AD2 follows the same slope as line AD1 but is plotted to the right.Points A and B are plotted along line AD1.Point A is a little less than half way along the left side of the line, and point B is little more than half way on the right side of the line.
-Refer to Figure 9.1.Ceteris paribus, an increase in households' expectations of their future income would be represented by a movement from
Definitions:
Restraints Of Trade
Legal restrictions placed on business practices that can limit competition or manipulate markets.
Economic Competition
The rivalry among businesses to attract customers and achieve a higher market share, driving innovation and efficiency.
Resale Price Maintenance
A practice where a manufacturer or wholesaler controls the retail price at which products are sold by retailers, often to maintain brand image or prevent price wars.
Anticompetitive Effects
Refer to actions or outcomes that reduce competition in a market, leading to less consumer choice and possibly higher prices.
Q24: Why are the long-run effects of an
Q28: If the multiplier is 5, the marginal
Q114: Refer to Scenario 10.2.As a result of
Q168: A major source of inefficiency in barter
Q168: The key idea of the aggregate expenditure
Q187: Which of the following is not a
Q194: You are an economic advisor to the
Q196: Long-run macroeconomic equilibrium occurs when aggregate demand
Q209: Deflation will<br>A)increase aggregate demand.<br>B)increase the quantity of
Q214: Planned aggregate expenditure is equal to<br>A)consumption spending