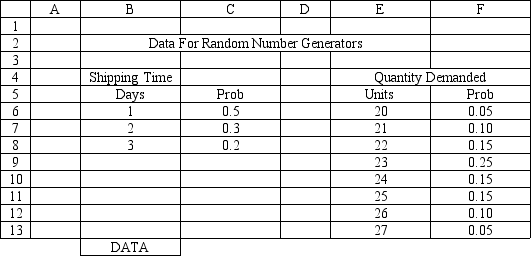
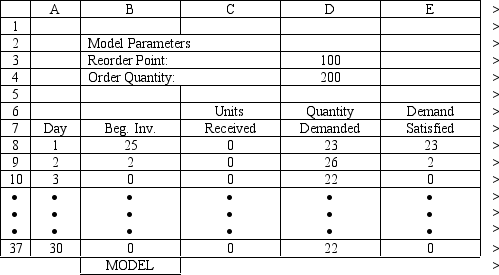
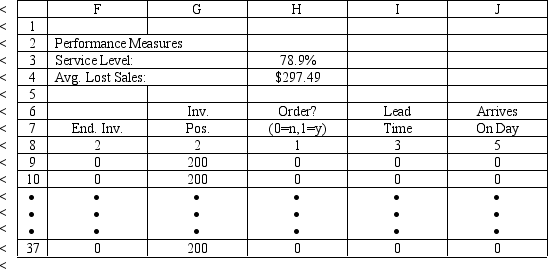
An office supply store wants to simulate its inventory system for notebooks. The company has collected data on the shipping time and daily demand for notebooks. Each notebook generates a $2 profit. Customers can buy notebooks at any office supply store so there are no backorders (the company loses the sale and profit). The company orders 200 notebooks whenever the inventory position falls below the reorder point of 100 notebooks. Orders are placed at the beginning of the day and delivered at the beginning of the day so the notebooks are available on the arrival day. The average daily demand is 23.5 notebooks. An average service level of 99% is desired. There are currently 25 notebooks on hand and no orders are pending. The following spreadsheets have been developed for this problem. The company has simulated 1 month of operation for its inventory system. (HINT: This covers Rows 8 to 37 of the spreadsheet.) What formulas go in cells A1:J37 of the "Model" worksheet for this simulation?
Definitions:
Interest Rate Parity Theory
Interest Rate Parity Theory is an economic theory which suggests that the difference in interest rates between two countries is equal to the expected change in exchange rates between their currencies.
Exchange Rates
The rate at which one currency can be exchanged for another, influencing international trade and capital flow between countries.
Equilibrium
In economics and finance, a state where supply equals demand, and market forces are in balance, resulting in stable prices.
WEBS Portfolios
WEBS Portfolios, originally known as World Equity Benchmark Shares, are exchange-traded funds that track international stock market indexes.
Q10: An investor wants to invest $50,000 in
Q12: One of PERT's bold assumptions is that<br>A)individual
Q15: <br>A common application of Monte Carlo simulation
Q21: Refer to Exhibit 9.3. What is the
Q22: Which of the following probability distributions are
Q30: Arturo transfers land with a FMV of
Q39: When using the GRG algorithm to solve
Q45: In NLP a local optimum is best
Q75: Refer to Exhibit 11.10. What formula should
Q80: Refer to Exhibit 11.14. What formulas should