In the presence of excess oxygen,methane gas burns in a constant-pressure system to yield carbon dioxide and water: 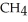 (g) +
(g) + 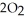 (g) →
(g) → 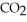 (g) +
(g) + 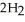 O(l) ΔH = -890.0 kJ Calculate the value of q (kJ) in this exothermic reaction when 1.70 g of methane is combusted at constant pressure.
O(l) ΔH = -890.0 kJ Calculate the value of q (kJ) in this exothermic reaction when 1.70 g of methane is combusted at constant pressure.
Definitions:
Individual Circumstances
Specific conditions or factors unique to a person's situation or case.
Indorser
A person who signs a negotiable instrument, such as a check, over to someone else, thereby making the recipient the legal owner of the document.
Secondary Liability
Legal responsibility of a third party for acts of another when that party has indirect involvement or benefits from the wrongful acts.
Without Recourse
A term indicating that the holder of a financial instrument cannot demand payment from the originator if the primary obligor defaults.
Q8: A solution is prepared by dissolving 98.6
Q32: Draw the Lewis structure for the molecule
Q41: Describe the greenhouse effect.
Q47: Determine the theoretical yield of H<sub>2</sub>S (in
Q55: Determine the partial pressure of oxygen necessary
Q80: Identify a substance that is in its
Q95: Calculate the change in internal energy (ΔE)for
Q102: An unknown substance has a boiling point
Q129: How much heat is absorbed/released when 25.00
Q153: Which of the following samples has the