Figure 3.2 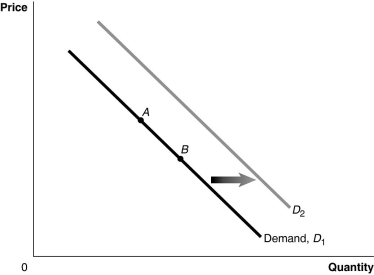 Alt text for Figure 3.2: In figure 3.2, a graph of the effect of an increase in the price of a complement on demand curve.
Alt text for Figure 3.2: In figure 3.2, a graph of the effect of an increase in the price of a complement on demand curve.
Long description for Figure 3.2: The x-axis is labelled, Quantity, and y-axis is labelled, Price.Curve Demand, D1, is a straight line which slopes down from the top left corner to the bottom right corner.Curve D2 follows the same slope as curve D1, but is plotted to the right.2 points, A and B, are plotted in the middle of curve D1.A right pointing arrow indicates the change from curve D1 to curve D2.
-Refer to Figure 3.2.If the product represented is a normal good, an increase in income would be represented by a movement from
Definitions:
Income Approach
A method of calculating GDP that sums up total national income, including wages, rent, interest, and profits.
Consumer Price Index (CPI)
An indicator used to gauge inflation by examining the weighted average prices of a selection of consumer products and services.
Circular Flow
A model that illustrates the movement of goods, services, and money among households, businesses, government, and the foreign sector in an economy.
Leakages
In economics, it refers to the withdrawal of potential spending from the economy's circular flow, primarily through savings, taxes, and imports.
Q33: Each person goes about her daily business
Q42: Prices of commercial airline tickets have fallen
Q49: Refer to Figure 3.1.An increase in population
Q66: Refer to Figure 3.3.An increase in price
Q110: Suppose that when the price of raspberries
Q124: Adam Smith,the father of modern economics,wrote in
Q141: In recent years the cost of producing
Q202: List the four broad categories of factors
Q217: In 18th century Europe,governments gave guilds legal
Q261: Using "chain-weighted" prices to calculate real GDP