A phase diagram of temperature versus composition for a mixture of the two volatile liquids octane (bp = 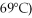 and decane (bp = 126°C) is shown.
and decane (bp = 126°C) is shown. 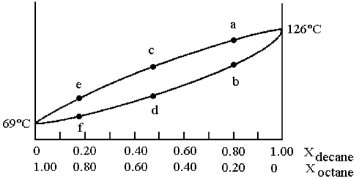
-Assume that you start with a mixture containing 0.80 mol of decane and 0.20 mol of octane,at what approximate temperature will the mixture begin to boil?
Definitions:
Normal Goods
Goods for which demand increases as the income of consumers increases.
GDP
Gross Domestic Product refers to the sum total of all monetary values of final goods and services produced within the geographical confines of a country during a given time frame.
Income Effect
The change in an individual’s or economy’s income and how that change will affect the quantity demanded of a good or service.
Substitution Effect
The change in consumption patterns due to a change in the relative prices of goods, leading consumers to replace more expensive items with less expensive ones.
Q2: For the reaction H<sub>2</sub>(g)+ S(s)⇌ H<sub>2</sub>S(g),if the
Q11: Intermediates occur at which reaction stages?<br>A)reaction stages
Q20: Which of the following forms an ionic
Q46: For the reaction shown below,if the rate
Q56: Freezing point depression,boiling point elevation,vapor pressure lowering,and
Q74: The first-order reaction,SO<sub>2</sub>Cl<sub>2</sub> → SO<sub>2</sub> + Cl<sub>2</sub>,has
Q75: The reaction below is first order in
Q78: Which nonequilibrium mixtures will react in the
Q111: If the units for rate are M
Q155: The action of some commercial drain cleaners