System 1 is 3.6 moles of a monatomic ideal gas held at a constant volume as it undergoes a temperature increase.System 2 is 3.6 moles of a diatomic ideal gas held at constant volume as it also undergoes a temperature increase.The thermal energy absorbed by System 1 is 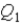
,and the thermal energy absorbed by System 2 is 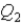
As both systems undergo a temperature increase of 74.6 K.What is the ratio 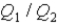
?
Definitions:
Deficient Fluid Volume
A medical condition characterized by a decrease in intravascular, interstitial, and/or intracellular fluid. This condition indicates dehydration.
Electrolyte Balance
The maintenance of the correct concentrations of ions in the body fluids, crucial for various bodily functions.
Respiratory Acidosis
A condition arising from the buildup of carbon dioxide in the bloodstream, leading to decreased pH levels and increased acidity.
Arterial Blood Gases
A test measuring oxygen and carbon dioxide levels in arterial blood to assess lung function and the body's acid-base balance.
Q6: System 1 is 3.6 moles of a
Q9: A sound wave in air has a
Q10: The bottom of a flat-bottomed aluminum boat
Q16: Bats can detect small objects such as
Q21: When a wool blanket is used to
Q40: A 2-m long piano string of mass
Q43: A steel wire,159 m long at 17°C,has
Q47: Why do vapor bubbles get larger in
Q52: As ice floats in water,about 10% of
Q66: I wish to use a positively charged