The fluorocarbon 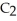
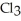
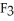 Has a normal boiling point of 47.6 °C.The specific heats of
Has a normal boiling point of 47.6 °C.The specific heats of 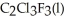 And
And 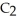
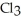
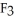 (g) are 0.91 J g-1 °C-1 and 0.67 J g-1 °C-1,respectively.The heat of vaporization of the compound is 27.49 kJ mol-1.The heat required to convert 50.0 g of the compound from the liquid at
(g) are 0.91 J g-1 °C-1 and 0.67 J g-1 °C-1,respectively.The heat of vaporization of the compound is 27.49 kJ mol-1.The heat required to convert 50.0 g of the compound from the liquid at 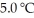 To the gas at 80.0 °C is ________ kJ.
To the gas at 80.0 °C is ________ kJ.
Definitions:
Endolymph
Fluid found within the membranous labyrinth of the inner ear.
Perilymph
The fluid that lies between the membranous and bony labyrinth of the inner ear, aiding in hearing and balance.
Oval Window
A membrane-covered opening that leads from the middle ear to the inner ear, vibrating in response to sound waves and transferring those vibrations into the cochlea.
Utricle And Saccule
Structures in the inner ear that are part of the vestibular system, helping to detect gravity and linear acceleration.
Q6: Choose the INCORRECT statement about CO<sub>2</sub>.<br>A)There are
Q51: Given the bond enthalpies C =C (611),C
Q62: For a reaction K<sub>eq</sub> = 1.2 ×
Q62: Which of the following molecules has both
Q63: Consider the reaction:<br><img src="https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB5343/.jpg" alt="Consider the reaction:
Q76: Which statement is INCORRECT about molecular orbital
Q105: Which of the following is an example
Q107: Moles of solute per liter of solution
Q113: For 2 NO<sub>2</sub>(g)⇌ N<sub>2</sub>O<sub>4</sub>(g),K<sub>c</sub> = [N<sub>2</sub>O<sub>4</sub>]/[NO<sub>2</sub>]<sup>2</sup>.At equilibrium
Q114: In a solution prepared by mixing equal