The equilibrium constant for the reaction C6H5COOH(aq) + CH3COO-(aq) 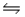
C6H5COO-(aq) + CH3COOH(aq)
Is 3.6 at 25°C.If Ka for CH3COOH is 1.8 × 10-5, what is the acid dissociation constant for C6H5COOH?
Definitions:
Physiological Responses
Physiological Responses are the body's automatic reactions to a stimulus, including changes in heart rate, breathing, and muscle tension.
Thalamus
A brain structure serving as a key relay station for sensory information, directing it to the appropriate areas of the brain for processing.
Amygdala
A small, almond-shaped cluster of nuclei located deep within the temporal lobes of the brain, involved in processing emotions such as fear, anger, and pleasure.
Cerebral Cortex
The outer layer of the cerebrum, involved in various high-level brain functions such as thought, memory, and consciousness.
Q6: The equilibrium constant for the reaction C<sub>7</sub>H<sub>15</sub>COOH(aq)+
Q6: Which one of the following is
Q20: What is the pH of a solution
Q61: At 25 °C, the base ionization constant
Q63: Calculate the pH of a 0.025 M
Q67: The solubility of silver bromide can be
Q82: Which one of the following reactions
Q98: Consider the reaction N<sub>2</sub>(g)+ 3H<sub>2</sub>(g) <img src="https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB3246/.jpg"
Q120: In the reaction: 2H<sub>2</sub>O(l) <img src="https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB3246/.jpg" alt="In
Q135: Which one of these statements about strong