The equilibrium constant for the reaction C7H15COOH(aq) + HCOO-(aq) 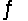 C7H15COO-(aq) + HCOOH(aq)
C7H15COO-(aq) + HCOOH(aq)
Is 7.23 * 10-2 at 25°C. If Ka for formic acid (HCOOH) is 1.77 * 10-4, what is the acid dissociation constant for C7H15COOH?
Definitions:
Predetermined Overhead Rate
A rate used to allocate overhead costs to products or services, calculated in advance based on estimated costs and activity levels.
Predetermined Overhead Rate
A rate used to allocate manufacturing overhead costs to products based on a pre-established criterion, such as labor hours or machine hours.
Direct Labor-Hours
The number of hours worked by employees directly involved in the production process.
Predetermined Overhead Rate
A rate used to allocate manufacturing overhead to individual products or job orders, based on estimated costs.
Q7: The pH of a 0.6 M solution
Q55: Which choice gives two raw materials used
Q57: Hydrogen iodide decomposes according to the equation:<br>2HI(g)
Q60: The measured voltage of a cell
Q63: Indicate all the types of intermolecular forces
Q64: The osmotic pressure of a 0.010 M
Q70: The molar enthalpy of vaporization of carbon
Q82: The vapor pressure of water at 20°C
Q90: K<sub>c</sub> for the reaction CO<sub>2</sub>(g)+ H<sub>2</sub>(g) <img
Q107: Consider the following standard reduction potentials in