The equilibrium constant at 427°C for the reaction N2(g) + 3H2(g) 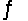 2NH3(g) is Kp = 9.4 10-5. Calculate the value of G° for the reaction under these conditions.
2NH3(g) is Kp = 9.4 10-5. Calculate the value of G° for the reaction under these conditions.
Definitions:
Weighted-Average Method
An inventory costing method that calculates the cost of goods sold and ending inventory based on the average cost of all units available for sale during the period.
Equivalent Unit
A concept in cost accounting used to allocate costs to partially completed units of production, treating them as an equivalent amount of fully completed units.
Prior Period Costs
Costs that were incurred in a previous reporting period and may be carried over into the current or a future period.
Job-Order Costing System
An accounting method that accumulates costs based on individual jobs or orders, suitable for companies producing unique or custom products.
Q8: Balance the equation <img src="https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB3245/.jpg" alt="Balance the
Q14: For the equilibrium reaction 2SO<sub>2</sub>(g)+ O<sub>2</sub>(g)
Q15: The solubility of Ba(NO<sub>3</sub>)<sub>2</sub> is 130.5 g/L
Q18: Consider the following equilibrium,<br>4NH<sub>3</sub>(g)+ 3O<sub>2</sub>(g) <img src="https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB3245/.jpg"
Q26: Hydrogen plays an important role in many
Q34: Nitrosyl chloride (NOCl)decomposes at elevated temperatures
Q60: You have 500.0 mL of a buffer
Q65: The compound CH<sub>3</sub>NH<sub>2</sub> reacts with water to
Q77: For the reaction Ni<sup>2+</sup>(aq)+ 2Fe<sup>2+</sup>(aq) <span
Q93: At 700 K, the reaction 2SO<sub>2</sub>(g)+ O<sub>2</sub>(g)