Calculate the equilibrium constant for the decomposition of water 2H2O(l) 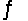 2H2(g) + O2(g)
2H2(g) + O2(g)
At 25°C, given that G°f (H2O(l) ) = -237.2 kJ/mol.
Definitions:
Genetic Variation
The diversity in gene frequencies within a population, which can result from mutation, sexual reproduction, and other processes.
Somatic Cells
Any cell of a living organism other than the reproductive cells; they make up the body's organs, skin, bones, and blood.
Cell Specialization
The process by which generic cells develop into specific types of cells to perform unique functions in the body.
Differentiation
The process by which cells become specialized in structure and function, acquiring characteristics distinct from the original cell type as they develop into various tissues and organs.
Q11: Ammonium chloride solutions are slightly acidic, so
Q14: Which is the most penetrating of the
Q21: The rate constant of the reaction
Q36: Which of these acids is stronger, H<sub>3</sub>PO<sub>4</sub>
Q39: Which one of these salts will form
Q42: Give (a)the oxidation number of the metal,
Q73: Write a net ionic equation for the
Q76: In the reaction H<sub>2</sub>CO<sub>3</sub> + H<sub>2</sub>O <img
Q76: Will a precipitate (ppt)form when 300.mL of
Q91: Consider a voltaic cell based on