Table 9.2
A firm has determined its optimal structure which is composed of the following sources and target market value proportions. 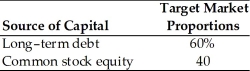 Debt: The firm can sell a 15-year, $1,000 par value, 8 percent bond for $1,050. A flotation cost of 2 percent of the face value would be required in addition to the premium of $50.
Debt: The firm can sell a 15-year, $1,000 par value, 8 percent bond for $1,050. A flotation cost of 2 percent of the face value would be required in addition to the premium of $50.
Common Stock: A firm's common stock is currently selling for $75 per share. The dividend expected to be paid at the end of the coming year is $5. Its dividend payments have been growing at a constant rate for the last five years. Five years ago, the dividend was $3.10. It is expected that to sell, a new common stock issue must be underpriced $2 per share and the firm must pay $1 per share in flotation costs. Additionally, the firm has a marginal tax rate of 40 percent.
-The weighted average cost of capital up to the point when retained earnings are exhausted is ________. (See Table 9.2)
Definitions:
Risk Premium
The extra return expected by investors for holding a risky asset over a risk-free one, serving as compensation for the additional risk.
Utils
A hypothetical unit of measurement used to quantify satisfaction or happiness derived from consuming goods or services.
Outcomes
The results or consequences of actions taken in a particular situation, often used in the context of strategies or experiments.
Utility Function
A mathematical representation that describes how the total utility or satisfaction a consumer derives from consuming goods and services depends on the quantities consumed.
Q9: The standard deviation of a portfolio is
Q22: Risk can be assessed by means of
Q29: Whole life policies are the most popular
Q63: As a bond approaches maturity, the price
Q89: Any action taken by a financial manager
Q114: Preferred stock has characteristics of debt since
Q116: Standard deviation is a measure of relative
Q121: When the constant-growth valuation model is used
Q149: What is Nico's portfolio beta if he
Q183: Given the following expected returns and standard